Circular saws with manual and mechanized feed
TO
category:
Carpentry work
Circular saws with manual and mechanized feed
Next: Ribbing and cross-cutting machines
Circular saw blades
The cutting tool on circular saws is the saw blade. Saw blades are distinguished by the profile of their teeth. The teeth are oblique with a straight, broken (wolf tooth) or convex back. The saw blade tooth profiles are shown in Fig. 1.
Saws with teeth with a broken and convex back, as they are more stable, are used for sawing hardwood. For sawing soft hardwood and softwood, saws with straight-backed teeth are used.
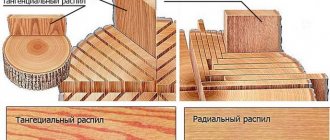
Rice. 1. Profiles of teeth of saws with a flat disk: a - for longitudinal sawing of wood, b - for cross-cutting, c - cross-cut velvet saw, d - longitudinal
To obtain a cleaner cut that does not require planing, a special type of circular saws is used - planing saws, or, as they are called, velvet saws. Their teeth are grouped and cut with combs. Each group has a large “working tooth” that produces cutting, and 3 to 10 small teeth located behind it. The diameter of planing saws is from 100 to 650 mm, the thickness of the gear rim is from 1.7 to 3.8 mm. They can be effectively used in all cases of longitudinal and transverse sawing, as well as sawing at an angle to the direction of the grain of softwood and deciduous wood. A particularly clean cutting surface is obtained when cutting parts from dry lumber. The shape of the teeth for longitudinal and transverse sawing is different and they do not move apart.
To cut the material strictly in a straight line into workpieces of a given width, there is a guide ruler on the machine table near the saw blade. The ruler is fixed at a distance from the disk that is equal to the specified width of the bars or workpieces being cut; the ruler also serves as a side stop when pressing the board during sawing.
Circular saws are produced by industry with balanced saws. In the future, due to their grinding, as well as due to the replacement of the working shaft, washers, nuts and others in the machine, the balance of the saws may be disrupted. Therefore, saws are checked on parallel horizontal balancing knives. The working shaft mounted on the knives with the saw blade mounted on it is rotated by hand around the axis of rotation, stopping it in various positions. If the shaft with the disk in the given position remains motionless, then it is considered balanced.
Manual feed circular saws
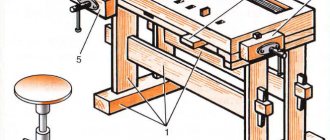
The circular saw shown in Fig. 2, used for longitudinal sawing of boards and bars. The cutting tool of the machine is a saw blade. Behind the saw blade, in the same plane as it, a riving knife is attached to the table to prevent the saw from being pinched by the board being cut.
This machine is of an outdated design, but since it is still used in large numbers at small woodworking enterprises, you need to know it. There are machines with manual feed of the latest design Ts-5 and machines of the latest production Ts-6.
The universal circular saw machine Ts-5 with manual feed is designed for longitudinal and transverse sawing of lumber. The saw shaft is driven by a V-belt drive from an individual electric motor. For work safety, a special saw blade guard is installed on the table. The lower part of the saw blade, located under the table, is covered with a casing that directs sawdust to the outlet. The support of the machine's work table can be moved in the vertical direction using the handwheel of the lifting mechanism. The machine is controlled by push-buttons.
Rice. 2. Circular saw machine for longitudinal sawing with manual feed: a - general view: 1 - work table, 2 - saw blade, 3 - riving knife, 4 - cap (casing), 5 - guide ruler, 6 - bed, 7 - receiver exhauster; b - riving knife
Rice. 3. Universal circular saw machine Ts-5: 1 - bed, 2 - saw blade guard casing, 3 - work table, 4 - slot in the table, 5 - upper saw blade guard, 6 - guide ruler, 7 - push-button control panel, 8 — handwheel of the lifting mechanism
Rice. 4. Universal circular saw Ts-6: a - general view; b - kinematic diagram of the adjustment mechanism: 1 - spindle, 2 - table, 3 - movable square, 4 - fence, 5 - guide ruler. 6 — handwheel for adjusting the saw support height; c — automatic feeder (view from the output side of the processed material)
The diameter of the saw is 500 mm, the number of saw revolutions per minute is 2800, the largest thickness of the sawn workpiece is 130 mm, the largest width of the sawed workpiece is 400 mm, the saw cutting speed is 73 m/sec, the number of electric motor revolutions per minute is 3000.
The universal circular saw machine Ts-6 with manual feed is designed for longitudinal and transverse sawing of lumber up to 400 mm wide and up to 130 mm thick. The machine has a saw spindle and a table along which it is fed manually. a workpiece, a movable support square for sawing across or at an angle, moved along a groove made in the table parallel to the saw blade, and a guide ruler. The saw is set to the desired height by turning the handwheel. A saw blade guard is installed on the table to ensure safe operation. When longitudinal sawing, universal machines should be equipped with automatic feeders that provide mechanized feeding of workpieces.
Rice. 5. Installation of the universal automatic feeder UPA-3
The universal automatic feeder UPA-3, produced by the Kurgan Woodworking Machine Plant, can also be used on a circular saw. It is installed so that three rollers are on one side of the disk, and three on the other. The automatic feeder must not be skewed, as this may cause breakage of the saw teeth. The pressure of the feed rollers, depending on the width, hardness and length of the board, is regulated by special springs, as a result of which slipping does not occur.
The automatic feeder not only protects the worker from accidents by covering the danger zone, but also makes work easier and increases productivity.
Nechunaev's guide ruler with a screw handle allows you to quickly set the feed to any width of sawn bars without stopping the machine. Its fixed bar 5 made of strip steel is tightly attached to the table top parallel to the saw blade. Two movable metal bars are hingedly connected to a third movable bar made of angle steel.
A wooden block is attached to the corner with screws, which serves as a guide for longitudinal sawing. If it is necessary to change the specified width of the sawn bars, the guide bar of the ruler is moved along the machine table by rotating the screw handle.
An addition to Nechunaev's mobile guide is a size ruler with a metric scale. It is fastened with screws flush with the plane of the table, strictly perpendicular to the saw blade and the guide ruler. The zero division should coincide with the right edge of the cut. With the help of a size ruler, the movement of the guide ruler is much faster.
By adapting various templates to the circular saw table, you can file tenons, select quarters and tongues, and chamfer.
Selection of quarters on a circular saw is shown in Fig. 7. Knives can have different profiles.
A device for cutting straight tenons and selecting lugs is shown in Fig. 8. The table stand with its supporting part is attached to the machine table. The angle of inclination of the installation plane to the table is chosen so that the cutting line is perpendicular to the edges of the workpiece. The tenons are cut with two saws mounted on the same circular saw shaft, at a distance from one another equal to the thickness of the tenon.
The eyes are selected with a swinging (“drunk”) saw. To obtain an oscillating saw, the saw blade is secured between two faceplates obliquely to the shaft axis. The angle of inclination of the saw to the shaft is taken such that in one revolution of the saw blade the eyelet is completely removed. The device is designed to process no more than two spikes or two eyes in a part. It is also used for sawing tenons in drawers and window frames.
Rice. 6. Nechunaev guide ruler with a screw handle: 1 - screw handle, 2 and 3 - movable bars, 4 - guide bar, 5 - fixed bar
The tenons and eyes on the circular saw are cut using templates.
Rice. 7. Cutting quarters on a circular saw: a - first operation, b - second operation, c - general view of the device; 1 - a lining that regulates the depth of cut on the small side of the quarter, 2 - a guide ruler with a recess in the lower part, 3 - the block being processed
Rice. 8. Device for cutting straight tenons and selecting lugs: 1 - workpiece, 2 - machined part, 3 - support block, 4 - guide bars, 5 - table stand, 6 - slot for saw
To select a tongue on a circular saw, a template is used, which consists of a board with a slot for the saw blade. The board is nailed to the bars so that the saw blade extends through the slot to a height equal to the depth of the groove. A guide board is nailed parallel to the saw blade at a distance from the disk equal to the thickness of the remaining wall of the tongue groove. For a more stable position of the guide board, a block is nailed to it, which is also fastened to the board. A cut equal to the width of the groove is made in one pass, for which the saw blade is installed so that it makes a “figure eight”.
The comb on a conventional circular saw is obtained in four passes.
For mass production of planed boards with a groove and tongue device, planing machines SK-15 and SP-30-1 and others are used, operating at a feed speed of 15 and 30 m/min. At the same time, the quality of the produced material is much higher. In addition, the labor consumption for performing this operation is significantly reduced and its cost is reduced.
When there is a small number of parts to be prepared or in the absence of four-sided planing and tenoning machines, milling machines are used to create grooves and tongues, tenons and eyes using the appropriate profile of cutter knives and devices - templates and jigs.
Rice. 9. Templates for selecting tongues and grooves on a circular saw: a - for selecting tongues and selecting scalene quarters: 1 - guide block, 2 - saw blade, 3 - beam; b - for making a groove: 1 - saw table, 2 - guide block, 3 - board, 4 - saw blade; c - for making tongue and groove: 1 - processed block, 2 - guide board, 3 - saw table, 4 - block, 5 - board, 6 - bars
Rice. 10. Device for cutting bosses: 1 - workpiece, 2 - machined parts, 3 - adjusting bolt, 4 - rotary stop, 5 - stop axis, 6 - slot in the slide, 7 - slide, 8 - guide grooves
To cut bosses on a circular saw, a special device is used, which is a slide with a rotary stop for the workpiece being processed. One end of the stop and the slide body have through slots through which an adjusting bolt with a head recessed in the slide body passes. The other end of the stop is mounted on the axis. The hinged connection of the stop with the slide allows you to install and secure the stop at any angle to the saw. When making bosses, the stop is set at an angle of 45°. Pressing the workpiece against the stop, feed the sled to the saw and make the first cut, then turn the workpiece over with the opposite edge and make a second cut to obtain the finished boss. The manufactured bosses have one angle of 90° and two of 45°.
The device is universal for bevel cuts and can be used to produce bosses with any angles and other similar products.
Circular saws with mechanized feed
In addition to circular saws with manual feed, there are circular saws with automatic feed, the productivity of which is many times higher, and the quality of the parts processed on them is much better.
The CA longitudinal circular saw with automatic feed is shown in Fig. 11. The machine has a roller-disc material feeding mechanism. The feed rollers and discs rotate from the saw shaft using various gears - belts, chains and gears. A corrugated feed roller protrudes from the plane of the table in front of the saw, and a toothed disk protrudes from above. Behind the saw there is the same device - a roller and a disk. The surface of the rim of this disk is grooved, and in the middle of the width of the rim along the entire circumference there is a roller that acts as a riving knife. Brake stops (thrust comb) are suspended in front of the front toothed disk, which prevent the material being cut from being thrown out of the machine and ensure the safety of the machine operator. There is an exhaust funnel to remove sawdust.
Rice. 11. Longitudinal circular saw machine CA with automatic feed: 1 - bed, 2 - suction, 3 - insert, 4 - feeding mechanism, 5 - saw guard, 6 - drive guard, 7 - ruler, 8 - handle for moving the ruler, 9 - control buttons
The circular saw with automatic feed TsA-2 differs from the TsA machine in the more closed form of the frame design. The material is supplied by rollers from a three-speed electric motor through a gearbox and chain drives. The machine is equipped with a claw curtain that prevents the workpiece from flying back, and a side guard for the saw. In addition, the machine is equipped with braking of the saw shaft.
The maximum thickness of the material cut on the machine is 80 mm, the minimum is 10 mm. The greatest width of the sawn material is 300 mm, and the shortest length is 665 mm. Feed speed 40; 51; 77 m/min. The largest saw diameter is 450 mm. The number of revolutions of the saw per minute is 2800. The machine is designed for longitudinal sawing of boards and bars.
Rice. 12. Notching machine TsDK-4 with caterpillar feed: 1 - bed, 2 - table, 3 - caterpillar, 4 - saw blade, 5 - pressure roller support, 6 - handwheels for setting the height of the saw support, 7 - handwheel for setting the height of the support pressure rollers, c - push-button station, 9 - stops that prevent the workpiece and scraps from being ejected from the machine, 10 - guide ruler
The single-saw cutting machine TsDK-4 with caterpillar feed has a saw blade located on top. This machine can be used to cut boards, planks, bars and panels. The material is fed to the saw blade by a caterpillar conveyor, ensuring straightness of the cut. The material is pressed against the conveyor by special rollers located in the support. The position of the caliper is adjusted depending on the thickness of the material using the handwheel. The saw is driven by an individual electric motor. The handwheel is designed to move the saw blade vertically. There is a 10 ruler on the table to guide the material. It can be set to the width of the board to the left and right of the saw. The machine is equipped with a protective device located under the conveyor, on the worker’s side. The largest diameter of the saw is 400 mm, the number of saw revolutions per minute is 3000, the material feed speed is 15; 22.5; thirty; 45 m/min. When speed sawing, the cutting speed can be increased from 50 to 100-150 m/sec. At such increased cutting speeds, thin saw blades are not permitted.
By type of woodworking equipment, the Scientific Research Institute of Woodworking Mechanical Engineering (NIIdrevmash) for 1961-1965. serial production of a multi-saw cutting machine with a diving caterpillar, model TsDK-5, is envisaged. This machine is compact in size and has high cutting and feed speeds. Board width up to 400 mm, feed speed with one saw 50, with three saws 20, and with five saws 10 m/min. Power 14 kW, weight 2.2 tons.
Preparing the tool for work
The saw blade sometimes has irregularities in the form of bulges and depressions, which are easy to detect if you hold a ruler to it. To straighten the disc, it is placed on a smooth metal plate or anvil and struck firmly around the bulge with a heavy hammer. When struck, the metal is stretched and the unevenness disappears. At the same time, it should be taken into account that the concavity of the middle part (dish-shaped) of the disk must be preserved. The teeth of the circular saw are aligned and sharpened on sharpening machines of various designs and on semi-automatic sharpening machines. After sharpening, lightly wipe the saw with an oiled rag.
The teeth of a saw with a flat disk are set apart after sharpening. The spreading of saw teeth consists of alternately bending the tops of the teeth in both directions. The size of the gap mainly depends on the nature of the sawing, the species and moisture content of the wood and should be no more than half the thickness of the saw blade. Saw teeth are set both manually and on machines. The RZP machine, one of the latest modern models, is designed for setting circular saws with a diameter of up to 1000 mm. The correctness of the divorce is checked using special templates and instruments. The greatest accuracy during testing is provided by indicator devices-water meters.
The teeth of planing saws and saws equipped with carbide plates are not set apart. They are supplied fully prepared for work with sharpened and polished teeth. Before installation on the machine, you only need to remove the protective anti-corrosion coating from them. Flat blade saws come from supplier factories with unset and unsharpened teeth. In this regard, each new saw at a woodworking enterprise must be sharpened and sharpened. It is especially labor-intensive to prepare saws with bevel teeth for cross-cutting.
Rice. 13. Installations for the restoration of circular saws
The saw must have sufficient stability during operation. Therefore, the amount of axial runout of its cutting rim is allowed to be no more than 0.5 mm, radial - no more than 0.05 mm. With proper sharpening and adjustment of the saw, the processed surfaces of the parts are very clean.
When restoring circular and frame saws with a thickness of up to 3 mm, a manual saw-stamp PSh-3 is used to cut new teeth on them. It consists of a cast iron frame and shaft. On one side, in the guides of the frame there is a slider with scissors, and on the opposite side there is a slider in which the punch is attached. The saw die matrix is mounted on a platform that is integral with the frame. The eccentric shaft is rotated by a long lever, which is fixedly mounted in the middle part of the shaft. To cut saw teeth, the stamp is installed so that the punch, fixed in the slide, when turning the lever, enters the hole in the matrix located on the bed. This ensures their exact match. After checking the match, the matrix is finally secured in the socket with set screws. Before pressing the lever when trimming a worn tooth or cutting a new one, the circular saw support and adjusting square are set depending on the diameter of the saws and the rake angle of the teeth, as well as the desired pitch of the teeth being cut.
To repair circular and frame saws with a thickness of up to 5 mm, a PShP driven saw blade is also used; the design of the machine is closed, with the drive mechanism located inside the bed. This gives the machine rigidity and vibration resistance and meets safety requirements. The saw die has a dividing mechanism that ensures notching of the teeth of circular saws in accordance with GOST 980-53 without preliminary marking. The rotation of the saws is done manually and is fixed.
Various pushers are used to feed sawn bars. This ensures safe work on circular saws.
When longitudinally sawing short parts on a circular saw, a guard designed by Toreev is used. The base of the fence is made of angle steel posts, to which the rear and front axles are attached.
On the front axle, the right and left sectors with teeth are mounted on hinges. A frame for guarding the rear part of the saw blade is also attached to the same axis.
Rice. 14. Safety pushers: a - an improved pusher with a metal fuse, b - a pusher mounted in the guide bar
Rice. 15. Guarding circular saws for longitudinal sawing of wood: 1 - counterweight. 2 — rear axle, 3 — lower angle, 4 — frame, 5 — connecting sector, 6 — left sector. 7 — cap, 3 — front pillar, 9 — front axle, 10 — right sector, 11 — sector ring, 12 — frame bushing, 13 — cap limiter
The cap covering the front and top of the saw is mounted on the rear axle and balanced by a counterweight. For stability of the fence axes and fastening of the cap limiter, the front and rear axles are connected by a sector. As the material is fed onto the saw blade, the cap rises with a slight push and allows the material to pass through. When the material comes into contact with the saw, toothed sectors located in the front part of the saw prevent the workpiece from being thrown back. This makes it possible to cut short workpieces. The rear of the saw is constantly covered by a guard frame, and when sawing, the guard automatically completely covers the saw blade. If the material is jammed by the sector teeth, lightly press the protruding upper parts with your hand.
Rice. 16. Organization of a workplace at a longitudinal circular saw machine
Thanks to the rigid mounting on the swinging bushing, the cap does not vibrate when working on the machine and makes it possible to make the fence relatively narrow - up to 20 mm.
The limiter allows the hood and rear guard frame to rise only to the specified thickness of the material being cut.
To support long timber when processing on circular saws, wooden or metal roller stands are used.
To rationally organize the workplace, the distance between the engine and the saw shaft must be reduced, and the machine table on the side of the auxiliary worker must be lengthened by 0.5-0.6 m, placing an electric motor under it. Boards to be cut should be placed on the right side. This will reduce the time it takes to move them from the stack to the table. The elongated table panel, supporting the workpieces from being overweight, reduces worker fatigue.
The side surfaces of saw blades must be smooth and free of cracks. Circular and band saws must not be missing two or more teeth adjacent to each other. In all cases, circular saws must be balanced.
When longitudinal sawing on a single-saw machine, a riving knife is installed behind the saw in the same plane with it. The height of the knife above the machine table should not be less than the height of the upper teeth of the saw, and the distance between the pointed part of the knife and the rear teeth of a saw of any diameter should not exceed 10 mm. The knife mount should ensure quick and easy rearrangement when changing saws, and also ensure that the knife is always in the plane of the cut.
Regardless of the use of riving knives on machines, safety stops must be installed in front and behind the saws.
The guide ruler should move easily along the table, be installed parallel to the saw blade, be easily and firmly secured in the required position and provide such fastening that eliminates the possibility of jamming of the material being cut.
The lower, non-working part of the saws (under the table), in the absence of an exhauster installation, must be covered with a continuous fence or two shields.
It is necessary that the peripheral speed of the saw teeth during longitudinal sawing be at least 50 m/sec.
The diameter of the saws on all machines must be such that the upper teeth protrude above the surface of the material being processed by at least 50 mm.
It is prohibited to simultaneously saw several workpieces in a stack without a special device that ensures they are pressed against the guide ruler and the table.
When working on circular saws with manual feed, the gap for the saw in the machine table should be no more than 10 mm. It is prohibited to saw material shorter than 300 mm or narrower than 30 mm without using special templates. Dividing coniferous boards with a thickness of no more than 100 mm into planks, and deciduous boards with a thickness of no more than 80 mm is allowed only if there are devices that press the sawn material to the ruler and to the table, and if a pusher is used.
When working on circular saw machines with caterpillar feed, the saw blade on the worker’s side must be protected by automatic movable guards, which at the same time prevent the ejection of the sawn material away from the saw.
Types of machines
An electric stationary circular saw is a fairly large-sized sawing unit with significant productivity and power coefficients. They are usually used in medium and large industries and factories for auxiliary operations. And in a home workshop and small production workshop, such equipment can also be useful as the main woodworking machine. The high speed of rotation of the saw shaft of these machines is ensured by a fairly powerful motor, which makes it possible to cut even hard material without overload.
A tabletop circular saw, like many woodworking machines for the home, can be installed on a workbench, and then, without any difficulties or associated problems, dismantled for use in another place or for storage. Typically, the weight of this equipment does not exceed 25 kilograms, which confirms its mobility.
Stationary household circular saw Bosch PTS 10
Both stationary and desktop versions include household and professional grade equipment. The differences between professional machines, in addition to cost, usually lie in their higher quality performance, and accordingly they have a longer working life, the presence of some additional accessories, and so on.
There are also multi-blade circular saws. They are usually used when it is necessary to longitudinally saw 2-edged and 3-edged beams with circular saws into edged boards and 4-edged beams. On multi-saw circular machines, you can make workpieces of different sizes by pre-setting the position of the saws. An important advantage of multi-rip circular saws is the fairly high cutting accuracy. This was achieved thanks to a significant increase in the strength of this equipment.
bed
It is the basis of any machine. The primary task is to provide an even, rigid and stable foundation for the remaining components of the equipment. As a rule, it is made of cast iron or steel. There are two types of base design:
- Cast - used for industrial machines, very heavy, extremely stable, floor-mounted.
- Welded - this type of base is used for light household machines; the main advantages are mobility and small size.
- Prefabricated ¬– is a stand made of bent or corrugated steel with stiffening ribs, also used for small machines.
Purpose of circular saws
A circular saw for wood is equipment that is used for transverse, longitudinal sawing of wood, as well as for its oblique sawing. In addition, if you have special discs, it is possible to work with other materials - plastic, aluminum profile, etc.
This equipment is best suited for cutting boards to size, making edges at 90º angles to each other, chamfering at different angles and creating almost all types of material joints.
Design Features
A sawing machine for wood, in principle, is a rather simple tool in its design, but it is still a high-precision tool, which is also a source of increased danger, so for its correct and safe operation it is necessary to have a good understanding of the design features of this unit.
So, there are four main types of circular saws:
- Manual portable cutting machines,
- Tabletop mini-circulars,
- Medium-sized circular saws with folding or removable stand,
- Large industrial stationary circular saw machines.
Manual portable cutting machines are not stationary equipment intended for use directly in the hands of a craftsman for cutting small boards, mainly on construction sites. This device weighs little and is quite compact and convenient equipment.
Tabletop mini-circular saws are also quite mobile equipment, since they do not have a heavy frame. Such a machine is installed on the top of a table or a homemade workbench, and after use it can be hidden in a pantry or utility room. These types of circulars are only suitable for amateur and household use due to their limited functionality.
A medium-sized circular table with a removable or folding stand, in most cases, is also equipped with prefabricated legs. This model is very compact and transportable and at the same time has greater capabilities than the previous type of machines.
Large stationary circular saws are used exclusively in large and medium-sized enterprises. For obvious reasons, such machines are absolutely not transportable and have all the functions necessary for professional use.
It is also important to note the fact that circular saws differ in the principle of saw blade arrangement:
- Vertical saw - a circular saw in which the working circle is located perpendicular to the working surface of the machine,
- Horizontal circular saws are equipped with a disk located parallel to the working surface,
- Coal sawing machines are equipped with two circles, which are installed at right angles to each other.
In any case, regardless of the type of circular, its design is based on a standard arrangement of elements. It consists of a frame on which a work table with a narrow oblong slot is mounted, through which part of the working cutting disk protrudes.
Depending on the configuration, the circular saw can be equipped with control and adjustment levers for the working elements of the machine, additional guides and stops, as well as measuring rulers, protection covers and other design elements designed to facilitate work and ensure safety standards.
bed
The bed is the basis of such a unit; its main task is to provide an even, stable and rigid support for the operation of the equipment. Depending on the type of machine, it is designed on one of three main types of bed:
- Cast - used for the manufacture of heavy industrial machines. It is made by casting metal from cast iron or heavy steel. Such a stand is practically non-transportable, heavy and bulky, therefore it is absolutely unsuitable not only for amateur use, but is also unsuitable even for small and medium-sized enterprises. This type of frame is installed on a very durable coating made of concrete and iron.
- Welded - made of thick-walled sheet steel. The weight of such a base is significantly less than the weight of a cast one, it is more mobile and is used to create equipment, mainly of the middle class, intended for medium and small-sized enterprises and workshops. It is not necessary to install the machine on such a frame on reinforced concrete; the base, however, must be quite strong and stable.
- Prefabricated structure made of metal profiles. This type of base is used in the manufacture of amateur equipment. It weighs little, and often even comes in a collapsible type. A machine built on the basis of such a frame can be placed in any type of room and on any surface. Mainly used on circular saws used in small home mini-workshops.
It is also important to note the fact that, regardless of the type of bed, in particular, and the circular machine, the most convenient to use is equipment with a sufficiently large working surface area, or the ability, if necessary, to expand it.
Working surface
The worktop tabletop is in most cases made of metal. It can be polished cast iron, steel or aluminum. Often, such a surface is supplemented with auxiliary guides and measuring equipment, which facilitate the work and increase its accuracy and quality.
In most cases, the part of the working surface directly with the working slot for the saw is a removable block, which is necessary for access to the saw for its adjustment, cleaning and maintenance.
The slot itself should be small in size to prevent excessive clogging of the saw and shaft with sawdust and dirt. If this condition is not met, and too much sawdust gets inside, it makes sense to make a homemade removable part from wood or plastic, and make the slot with the saw itself during the installation process. It is important to be extremely attentive and careful.
Disk
Depending on the type of circular saw and the type of lumber being processed, circular saw wheels of various diameters and with different tooth configurations can be used.
The diameter of such a circle can vary from 140 to 300 mm. On professional equipment, circles with a size of 250 mm or more are mainly used, and for amateur use, smaller circles are used. The main factor that determines the size of the wheel is the maximum depth of cut of the material being processed; it also depends on the height of the protrusion of the wheel above the working surface. In most cases, the height of the disc protrusion is no more than 1/3 of the diameter of the disc itself.
Most models on the circular saw market provide the ability to tilt the blade at an angle of up to 45 degrees. But in this case, you need to be extremely careful, since in some models this requires lowering the wheel to a certain level, or even removing the removable part of the worktop, so you should first read the operating instructions for such a machine.
To increase the service life of the saw blade and perform a higher-quality cut, you need to adjust the disk so that its teeth protrude above the lumber during operation at an average level of 7-9 mm.
Protective equipment
As already mentioned, a circular saw is not only useful equipment, but also very dangerous. It is for this reason that almost all models of such devices are equipped with a special protective casing. This detail is designed to prevent dangerous contact of the material being processed with parts of the body of the master working with it. The casing is mounted on a special bracket, which allows you to adjust the height of its landing, or remove the casing altogether if necessary.
Safety riving knife
In some cases, the material being processed has hidden invisible defects and differences in the strength of the layers. This may be a consequence of the natural characteristics of the wood or a violation of the technology of its drying and storage.
In such cases, the board being sawed can split and jam the disk rotating at fairly high speeds, as a result of which a very sharp ejection of material can occur directly onto the master. To prevent this from happening, manufacturers have included a special wedging element in the design of the circular saw, which is installed directly behind the disk and does not allow sawn parts of wood to connect.
Rip fence
Wood circular saws are used to cut wood at different angles and in different directions. Therefore, they are also suitable for longitudinal dissection of logs into boards or beams, as well as for cutting various wood boards such as chipboard or OSB into long strips.
In order for longitudinal cutting to be smooth and accurate, the manufacturers of such machines have included in their design such a device as a stop for longitudinal cutting.
The stop must be securely and stably attached to the working part of the machine at at least two points, and not bend or bend during operation. The design of this device should include the ability to adjust the distance from the working disk to the stop; ideally, a sheet of chipboard or other similar material should be placed between them.
Stop for cutting at an angle
This device is located perpendicular to the saw blade, with the ability to adjust it at different angles ranging from 90 to 45 degrees. For ease of regulation, a special graduated scale should be provided.
With the help of such an element it is possible to accurately determine and adjust the angle of the transverse cut of lumber. The emphasis must also be stable and reliable and attached in several places.
Powerplant and drive
As with any other power tool, one of the factors determining the functionality is the power of the machine’s power unit. After all, to work with large-sized lumber and sawing hardwood, you need a fairly powerful engine and a reliable drive.
In most cases, circular machines are equipped with fairly powerful motors ranging from 1200 to 3000 W. For the manufacture of low-power circular saws, electric motors with a power of 1200 - 1500 W are used, and for middle-class machines and large industrial saws I use motors of 1500 W and higher.
The power plant and drive of an electric circular saw consists of an electric motor, a shaft on which the saw blade is mounted, and a drive connecting these two components. For low-power hand-held cutting saws, a gearbox with a gear drive is used.
Technical characteristics of circular saws
Main technical characteristics that you should pay attention to when choosing a circular woodworking machine:
- power;
- depth of cut;
- spindle rotation speed;
- desktop size;
- bed (steel, cast iron, stamped sheet);
- saw tilt, (90º, 45º);
- voltage (220 V, 380 V).
Now let's look at some of them separately.
The greater the power, the greater the amount of work that can be performed on a circular saw; this also allows you not to reduce the speed when sawing, install disks of increased diameter, if the design of the equipment allows them, and in addition, the working life of the product increases.
The depth of cut affects the size of the workpiece and miter cuts.
The number of rotations of the spindle - the higher, the higher the quality and cutting speed of the sawing machine.
The size of the workpiece that can be processed depends on the size of the work table.
An important characteristic of circular machines is the material of the machine bed. More powerful, heavier and professional models usually use a closed steel tabletop, which improves dust collection and reduces noise from the saw blade and electric motor. Lightweight circular saws are often equipped with cast iron frames. The weighted design reduces vibration and keeps settings accurate longer than those with stamped steel fenders.
Voltage. Electric motors over 2 hp Usually they use three phases of 380 V power supply; less powerful ones most often make do with single-phase 220 V power supply. Therefore, before choosing equipment, you need to clarify how many phases you have at the connection point of this machine.
Preparing for work
Before you begin, you need to decide on the necessary set of tools and materials that will be needed during the work process.
The following tools will be used for work:
- A circular saw or you can use a jigsaw.
- Screwdriver.
- Grinding machine.
- Grinder (Angle grinder).
- Jigsaw.
- Hand tools: hammer, pencil, square.
During the work you will also need the following materials:
- Chipboard.
- Plywood.
- Solid pine.
- Steel tube with an internal diameter of 6-10 mm.
- Steel rod with an outer diameter of 6-10 mm.
- Two washers with an increased area and an internal diameter of 6-10 mm.
- Self-tapping screws.
- Wood glue.
Design of a circular saw stop
The entire structure consists of two main parts - longitudinal and transverse (meaning relative to the plane of the saw blade). Each of these parts is rigidly connected to the other and is a complex structure that includes a set of parts.
The main technological solution of this stop is the principle of jamming using an eccentric and tightly pressing two transverse guides with an oblique end.
Fixation occurs by turning the eccentric mechanism.
The pressing force is large enough to ensure the strength of the structure and securely fix the entire rip fence.
The entire design is not trivial and consists of a large number of different parts, each of which has its own purpose and size.
From a different angle.
The general composition of all parts is as follows:
- Transverse part
- The base of the transverse part;
- Upper transverse clamping bar (with an oblique end);
- Lower transverse clamping bar (with an oblique end);
- End (fixing) strip of the transverse part.
- Longitudinal part
- Planar sliding element (laminated chipboard, 2 pcs.);
- The base of the longitudinal part;
- Clamp
- Eccentric
- Eccentric handle
Stationary equipment
Stationary circular saws are quite large. They are suitable for use by industrial companies performing impressive volumes of lumber processing. The engine has great power. The cast iron bed lasts a long time because its strength is above average. It is permissible to process hard wood when it is necessary to cut with a depth of 70–125 mm.
Equipment for the production of lumber
Designs on an extended bed represent a middle-class category, complemented by a convenient stand - a practical extension table on which a plane can be placed very easily. Such a unit is distinguished by significant power when compared with household analogues, and the cutting depth reaches 80–90 mm, that is, workers can easily saw workpieces of impressive sizes.
It is better not to buy the offered equipment on the markets. It must be guaranteed to be safe. It makes sense to look for professional stores that offer long-lasting models that will last for several years with intensive use.
Manufacturers and models of installations
When deciding to purchase a unit, you need to pay attention to manufacturers and consumer reviews.
The leader in the woodworking equipment market is Bosch. It offers both industrial and household machines. The units have the following capabilities:
- laser unit;
- broach;
- cutting depth adjustment;
- a large number of revolutions.
One significant drawback of Bosch installations is the high price.
The German company Metabo produces high quality machines with a large number of functions. Models from this company have the functions of extending the table and cutting chipboard. There are models for sawing high-strength and large-sized materials.
The model that is assembled in China is a Hitachi unit. This is inexpensive, high-quality equipment for household use in a gentle manner. The motor power is 1600 W, its cutting depth is 73 mm, and the rotation speed is 4800 rpm.
The Japanese company Makita produces over twenty modifications of units. The Makita circular saw is designed for high-precision work. Thanks to the electric motor braking function, the safety of using the unit increases. The advantages of this model include a movable folding bed, increasing the working surface by extending it back and to the right.
Which wheels to take?
The saw blade is the most important part of the circular saw, the working part for which it is made. The entire design of the machine is also tied to it, so we need to decide in advance which disks we will use in our work, and how to choose the right one in absentia (online) according to the designations on it or in the description..
Types and designation systems of saw blades
The most common 2 notation systems. According to the first (item A, position 1 in the figure), the following are sequentially designated:
- diameter of the disk at the tops of the teeth, mm;
- cutting width, mm;
- diameter of the installation (landing) hole, mm. Typical (default) tolerance +0.05 mm is not specified;
- atypical landing tolerance (possibly);
- number of teeth;
- the letter T or pictogram - the presence of carbide tipped on the teeth;
- rotation speed - operating (nominal) simply in numbers, the maximum permissible with the prefix max.
According to the second system, it is mandatory to indicate the standard size of the disk in numbers separated by hyphens: diameter at the bases of the teeth, their number, landing diameter (the default tolerance is the same). For example, 190-36-30 in item B, pos. 2 means a disk with a diameter of 190 mm (at the tops of the teeth there will be 200) with 36 teeth for a 30 mm fit. The rotation speed is indicated separately, but here it is the maximum by default; labor is 10% less. The remaining parameters are indicated either by symbols (item B, item 2) or textually. The minimum rotation speed, at which proper cutting quality is still ensured, for certified disks with stabilizing slots (items 1, 2, 4, 5) is 50% lower than the working one, and for solid disks it is 25% less.
There are quite high-quality “non-system” disks on sale (items 3-5). But in all cases, simply “for wood” (items 2-4) means commercial wood, plywood, chipboard, laminate and other fairly high-quality wood materials corresponding to the specifications. It is dangerous to saw unseasoned raw wood with such a blade - it can jam and fly apart. For sawing wild wood, special discs are produced with the designations Forest (forest, item 5), Wildwood (wild tree), Timber (wood), Log (log), etc. Discs with such designations are used in stationary pendulum saws, circular sawmills and other equipment for sawing raw wood.
Note : if you are going to saw metal with a circular saw, be careful - discs for steel and aluminum are not interchangeable. Universal discs for sawing any materials are also sold, but they work roughly. It is impossible to saw laminate, chipboard and other laminated materials with “station wagons” - the coating will peel off.
Finally, many saw blades go on sale without any markings or pos. 6 in Fig. In general, they cut, but you need to be careful with them: it is better not to give the linear speed of rotation of such a disk more than 40 m/s. To obtain the rotation speed from it (to calculate the gear), we measure the diameter of the disk at the bases of the teeth D (in mm), and calculate its operating rotation speed as 60(40,000/(3.1415xD)). For example, the operating speed of rotation of a “cloudy” disk of 200 mm will be 3815 rpm; It's better to take 3500.
And one more device
But what if you need to cut the workpiece across or at an angle? Making a cutting machine? Perhaps with your own hands, but for thin workpieces (boards, parquet, laminate, door frames) it is not necessary.
For such purposes, there are transverse/angular carriages for circular saws.
Design and drawings of transverse/angular carriages for a circular saw
If there is a milling table or access to it, then select a longitudinal groove in the tabletop (removed from the machine) and make an angular stop for it (top left in the figure); The arrow shows the direction of feeding, and during it the workpiece is pressed against the stop. If not, you can make a transverse carriage (bottom left and right, drawings); perhaps with a focus on the most sought after fixed angle of 45 degrees. For cross-cutting, the board is laid along the carriage; for cutting at 45 degrees - with a skew. The carriage is moved so that the saw blade passes through the slot in it, that's all. It’s not very good that a lot of cutting depth is lost, but when the disc reaches 50 mm, boards up to 20-25 mm thick can be sawed. Additionally, a video on how to make a transverse carriage for a circular saw: