08/30/2021 Author: VT-METALL
Issues discussed in the material:
- Types of fasteners for joining metal
- Recommendations for choosing fasteners for connecting metal products
- 6 ways to join metal products
- Areas of application of various methods of joining metal products
Today, the construction industry provides a wide selection of all kinds of fasteners and methods for combining various materials. But not everyone knows what methods of joining metal products there are, although this information can be very useful, because the areas where this is relevant are numerous and varied.
In our article, we presented an overview of the main methods by which metal parts are connected, indicating their key features. We also listed the main fasteners that are used for this purpose, so the information awaits you extremely useful.
Types of fasteners for joining metal
To connect products to each other, metal fasteners are used, available on the market in a wide range. Fasteners have different sizes, shapes and purposes. Most often, parts are connected with screws, bolts, nuts, self-tapping screws, screws, anchors, rivets, studs, washers, etc.
1. Bolt.
One of the ways to connect metal products is through bolts - rods with external threads and a four- or hexagonal head. The connection requires a nut or a hole with internal threads. The bolt resembles a screw in appearance; both fastening elements are widely used in mechanical engineering, construction, etc.
They differ in the way they work:
- the bolt passes through the elements to be connected and is fixed with a nut or wrench;
- the screw is screwed into the threaded part using a screwdriver or socket wrench.
Unlike the second, the first does not scroll inside the connected elements.
We recommend articles on metalworking
- Steel grades: classification and interpretation
- Aluminum grades and areas of their application
- Defects in metal products: causes and search methods
2. Self-tapping screws.
Self-tapping screws are often used to connect wooden parts:
- fasteners with fine threads connect metal blanks of small thickness to wooden or plastic parts;
- self-tapping screws with large threads are designed for fixing wooden parts.
The sharp tip, made in the form of a drill, independently makes holes in the workpieces to be joined.
3. Nut.
Another way to connect metal parts is using nuts - fasteners with a hole and internal thread. Used in conjunction with bolts. Nuts vary in shape (hex, knurled round, square, T, finger lug, etc.) as well as strength.
4. Screw.
This fastener is a rod with an external thread, a conical tip and a head. The method of connecting metal to each other using screws is to screw the fastener into a finished hole or soft material (plastic, wood). This is the difference between them and self-tapping screws. They are less universal compared to the latter, as they have a smaller height and thread pitch. This type of fastener is in demand in construction and finishing works.
5. Anchor.
The anchor is attached to the supporting base and holds the desired element. The fastener has two parts:
- non-expandable, which is not directly involved in fixing structures;
- spacer (working), with variable dimensions.
In addition to the main parts, it may have a cuff - a border that prevents penetration into the base or fixed structure. Anchors are used for connecting metal products made from sheet materials, as well as for fastening heavy structures and foundations.
6. Rivets.
They are divided into two main types:
- Exhaust, consisting of an aluminum head and a galvanized steel rod. They are designed to permanently fix two or more metal elements. When working with them, mechanical tools are used.
- Threaded rivets are widely used in mechanical engineering and electronics. The shaft of this fastener is threaded, so the parts connected with it can be disassembled if necessary.
7. Hairpin.
This is a cylindrical rod without a head with threads along the entire length or only at the ends. This method of connecting metal products is used when there is no thread on the parts being fixed. Used in conjunction with a nut, or can be supplemented with a washer. The latter is a round plate placed under the nut and increases the strength of the fastening, preventing deformation of the workpieces being connected. This is achieved by increasing the pressing surface of the parts being fastened.
Pins are used to fasten any products and structures, including highly loaded ones. The advantage of this method of fastening metal elements is that its use does not require special skills.
Depending on the presence of threads, fasteners are divided into:
- metric, represented by screws, bolts, nuts and studs;
- non-metric (adapted), represented by nails, anchors, etc.
Depending on the area of use they are divided into:
- high-strength threaded fasteners;
- elements of mass use;
- products for shockless and/or unilateral fixation;
- fasteners intended for sealing products;
- parts intended for joining polymer composite materials, etc.
This is a conditional classification, since fasteners can simultaneously belong to several groups.
Groove and side tongue joints
This is a combination of a quarter cut and a rebate cut. It is used in the manufacture of furniture and the installation of slopes for window openings.
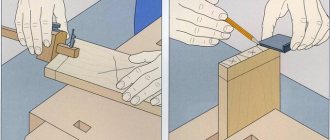
Making a connection
1. Make the ends perpendicular to the longitudinal axes of both parts. Mark the shoulder on one part, measuring the thickness of the material from the end. Continue marking on both edges and the front side.
2. Mark the second shoulder from the end side; it should be at a distance of one third of the thickness of the material. Continue on both edges.
3. Using a thickness gauge, mark the depth of the groove (one-third of the thickness of the material) on the edges between the shoulder lines.
4. Using a hacksaw, saw through the shoulders to the thickness line. Remove waste with a chisel and check the alignment.
5. Using a thicknesser with the same setting, mark a line on the back side and on the edges of the second part.
Adviсe:
- Mortise and tongue-and-groove joints can be easily made using a router and a suitable guide - either for the groove only, or for both the groove and the tongue. Recommendations for proper operation of the router, see p. 35.
- If the comb fits into the groove too tightly, trim the face (smooth) side of the comb or sand it with sandpaper.
6. From the front side, use a thicknesser to mark the edges towards the end and at the end itself. Saw along the lines of the planer with a hacksaw. Don't cut too deep as this will weaken the joint.
7. Using a chisel from the end, remove the waste. Check fit and adjust if necessary.
Recommendations for choosing fasteners for connecting metal products
Various methods of joining metal products are used in a wide variety of industries and production: from the creation of electronic devices to construction. After treatment with special compounds that increase their strength and anti-corrosion properties, fasteners are suitable for use in aggressive environments, in conditions of high humidity.
The service life of the finished product or structure also depends on the fasteners used, so when choosing them you should pay attention to the following:
- the strength of the fastener must be higher than the strength of the workpieces being connected;
- high tightness, regardless of the object at which one or another fastener and/or method of connecting metal products is used;
- high-quality materials, thanks to which high reliability and safety of the finished structure is achieved;
- the type and diameter of fasteners are selected in accordance with the expected nature of the impact (transverse or longitudinal, static or dynamic).
Advantages and disadvantages of steel fasteners
In mechanical engineering, instrument making, furniture production, construction and other industries, fasteners made of steel and its alloys are most often used. They equally effectively connect parts made of wood, metal, plastic, concrete and other materials.
Steel fasteners are characterized by high strength, low metal fatigue, excellent electrical conductivity and an affordable price. Under high loads, steel fasteners do not change their shape like plastic ones and do not break like cast iron ones.
Ordinary carbon steel has low resistance to corrosion, so alloy steel (with the addition of chromium, nickel, silicon, molybdenum and other elements) is used to make fasteners.
Steel with an admixture of chromium (> 10.5%) and a small amount of carbon (< 1.2%) has high anti-corrosion properties.
Stainless steels include austenitic steels containing chromium and nickel. They can be welded, cold worked, hot worked. A wide range of advantages makes them the most popular for the manufacture of fasteners. In classifiers, this group of steels is designated by the letter “A”.
Martensitic steels (“C”) are strengthened by quenching followed by tempering, as a result of which they acquire greater hardness than austenitic steels. Their corrosion resistance is lower.
Ferritic steels (“F”) are much softer than martensitic steels due to their low carbon content. However, they have magnetic properties.
Areas of application of various methods of joining metal products
Various methods of fixing metal elements are used in different areas of industry, as well as in everyday life. They are used in furniture production, construction, heavy industry, etc.
Keyed and splined fasteners are common in the areas of creating power tools, equipment, and mechanical engineering. Without interference joints it is impossible to produce gear shafts and worm wheels. Soldering is necessary for working on electronic equipment that requires high precision. Rivets are used to connect thin sheet metals.
As technological progress develops, new ways of joining metal products appear. Modern life is impossible without various machines and mechanisms. In order for them to last longer, reliable fasteners are needed. The quality of fasteners also determines the shape of the finished product, the quality of its work, the risks of accidents and emergency situations in production, etc.
In the article we talked about the types and methods of connecting metal products and parts. Before purchasing any fastener, you should inspect it for defects. Parts deformed during operation can be used for the outer contours of metal workpieces. Thus, savings on consumables are possible, but without compromising the quality of the finished product.
Forming miter angles
One of the best ways to create corners of various volumetric products is a miter joint. It allows you to create a monolithic structure, hide the fibers of the end, thereby providing an attractive appearance. This method is suitable for a wide variety of products, but is most often used for the manufacture of frames and cabinet furniture parts.
To create a joint, cuts are made in each of the wooden parts at an angle equal to half the angle at which the workpieces meet. Most often, this angle is right, therefore, cuts are made at 45 degrees, however, the angle can vary widely. The work is performed according to the following algorithm.
First, mark out the details. It is important not to forget that the markings are made along the long side, otherwise you may not guess with the dimensions.
On the edges that will be connected, draw a line at the required angle. Using a combination square, the markings are transferred to each side of the workpiece. Then the cut is made, for which it is better to use an electric miter saw, but you can also work with a hand tool. When working with a hacksaw, it is important to control the cutting angle; it would be useful to use a block as a guide.
The finished parts are placed next to each other, checking the accuracy of the fit. Unevenness will have to be smoothed out with a hand plane, and the angle will have to be adjusted using sandpaper. Wood glue is applied to both surfaces, and the product is fixed using clamps. Additional strength can be achieved using nails. When working with a hammer, it is important to control the impact force so that the workpieces do not move.
Particularly critical connections are reinforced with bars that are glued into the inner corner. A joint that will not be visible can be additionally reinforced with a metal square.
The result of quality work will be a perfect seam. If a small gap has formed, it can be hidden by straightening the adjacent wood fibers using a smooth cylindrical surface. The shaft of a regular screwdriver is suitable for this.
Placing the boards together
High-quality wood is expensive, and it is not always possible to buy a good board with the necessary parameters, and it is not always necessary. To make, for example, a tabletop, it is not at all necessary to look for a table-wide board; with carpentry skills, you can create an ideal wooden sheet with the necessary parameters.
There are many options for bonding. A board with a tongue and groove, the so-called lining, is widely used. It allows you to create smooth wooden surfaces of a large area. A simplified version of it is often used - a board with a quarter joint.
Joining on a smooth fugue (butt)
The simplest method that does not require additional elements. The side edges of the boards are jointed; it is better to do this in pairs, clamping both adjacent boards in a vice and processing them at the same time. This treatment will create a precise surface on which the unevenness of one board will be compensated by the unevenness of the other. Both boards are coated with glue and fixed until it hardens completely.
Using additional connections
This method provides a more reliable design, but is not particularly complicated. The boards for it are also leveled, but symmetrical holes are made in the connected ends for installing dowels or pins. It is possible to strengthen the resulting fabric using driven-in metal staples. Of course, the staples are driven in from the inside of the product.
Bonding load-bearing elements
There are several ways to lengthen (build up) a board that is part of the supporting structure. The simplest and most reliable is a half-timber connection followed by overlaying reinforcing strips at the junction. Non-critical areas can be reinforced with plywood.
The same method is also used to join boards at different angles. Precisely made cuts of the jointed parts make it possible to do without reinforcing linings; it is enough to secure the boards at the joint with screws.
Let's look at the most common fastening hardware
Bolt - is a fastening device for a detachable connection, which is essentially a rod with a thread at one end and a special head at the other (usually 4 or 6-sided).
For the production of bolts, low-alloy, carbon steel, or special steels are used; brass products of other materials are also found.
The thread on the bolt is intended for screwing on the nut.
Bolts are produced with both full and partial threads (relative to the length of the bolt shaft).
Staples
This type of hardware is used according to the principle of a nail. The brackets are U-shaped elements. They are mounted in soft surfaces of structures. The staples are designed for wood joints, MDF or plywood. For convenience and proper installation, use a construction stapler. It can be used to make reliable connections. Staples are often used in construction and furniture assembly.
Cotter pins
These are hardware that have a characteristic eye at one end. The main purpose of such hardware is to prevent self-loosening of bolts and nuts. Initially, the cotter pins are bent to the desired shape to make it convenient to use with other types of fasteners. This type of fastening is used in the construction industry. Cotter pins are characterized by relative flexibility. Universal application and low cost determine increased demand for this category of goods.
The cotter pins are easy to install; you don't even need special tools. Depending on the technical requirements and fastener features, you can choose the appropriate type of cotter pin. Most often, products are made of stainless, carbon and alloy steel. These materials can withstand heavy loads and provide durable corrosion protection.
Plan your assembly sequence carefully
You have carefully cut out all the parts, achieved tightness in all joints and are now ready to start assembling. But before you open the glue bottle, be sure to do a dry assembly test (without glue). When assembling the product, determine in what order it is best to connect the parts, how many clamps will be needed to tightly compress all the joints, and how best to place the clamps so that there are no distortions.
It's best to break up large, complex projects into several simple steps instead of rushing around trying to glue all the pieces together in one go. For example, when making a cabinet with paneled sides, first assemble the frames with panels, and then proceed with the main assembly. This approach gives you more time to check all connections and requires fewer clamps. Another way to gain time is to use glue with an extended setting time. For example, regular yellow Titebond glue allows you to complete the entire assembly in 15 minutes, and the Titebond Extend variety allows you to level the glue within 25 minutes.
When installing clamps, make sure that their pressure is applied to the middle of the connection. An incorrectly installed clamp can deform the parts so that a gap forms between them. Sometimes, despite all efforts, the connections do not turn out neat. An accidentally slipped tool, inattention, or undetected sawdust near the stop lead to a loose connection or a noticeable gap in it.
Assemble the cabinet in stages, first gluing together the small side panel frames. Then you can pay more attention to each connection. Then start assembling the case
Anchors
In their design features they resemble a dowel-nail. The anchor consists of a dowel and a bolt. When the bolt is screwed in, the walls of the dowel expand. Anchors are used to secure large and heavy objects. There is a whole list of types of anchors.
Compression anchors are installed on ready-made non-demountable structures. When installing the frame, a tight fit is ensured between the three parts of the frame - the head, the stop and the hinges. Masonry anchors are used on frames attached to a brick block wall. Anchors with steel studs are attached to steel bases. Wood dowel anchors have one thing going for them: the anchor has clips that are used to wrap and secure it to the wood dowel during installation.