- Methods for joining wooden parts:
- Gluing
- Connection with nails
- Connection with screws and self-tapping screws
- Types of connections of wooden parts
- Connection examples
- Butt connection
- Miter
- Reinforced wire connection
- Rallying end to end
- Rallying in a quarter
- Half-tree connection at an angle
- Half-wood overlay connection
- Angled connection with a through tenon
- Joining at an angle with a through tenon
- Joining at an angle with a hidden tenon
- Box dovetail connection
If you need to make a stronger connection than with nails, then use screws or self-tapping screws. It takes longer to do than connecting with nails, but it is more reliable. When working with wood, nails do not provide the freedom of action that self-tapping screws can provide.
For example, if you screwed or nailed something incorrectly, it is easier to correct the mistake by unscrewing the screw back. When removed, the nail will bend and most likely will no longer be suitable for use. It is much more difficult to pull the self-tapping screw out of its fastening point, but it may break when torn off. At the same time, as mentioned above, it is easier to unscrew it and screw it into another place than a nail.
When choosing a screw, you need to take into account that its length should be 2-3 times greater than the thickness of the thinner part to be connected. In this case, the screw should not go through the main (thicker) part.
Types of joints of wooden products
The joining of wooden parts, depending on the means of connection used, is divided into:
- Non-glued joints with the possibility of subsequent disassembly. Nails, staples, screws, bolts, connecting fittings are used);
- Adhesive joints - created either with simple glue or with the help of other inserted elements (pins, handles, slats, etc.). Such connections are inseparable;
- Butt joints - when grooves and inserted parts are adjusted with high precision and good deformation resistance, followed by self-locking.
Application
The use of dowels for timber is very limited. With its help, wooden buildings are built. That is why installation features are associated with laying timber or logs. Holes for fastening are drilled through the top of the log, and only halfway from the bottom. The nest is made vertically.
The beam must slide along the rod during the shrinkage process. The holes should be centrally located. The dowel for the timber is usually installed at a distance of 50 cm from the corner. The remaining holes are made in a checkerboard pattern. The minimum distance between them should be 150 cm.
Non-adhesive connections
Nailing - In carpentry, nails secure cabinet backs, drawer bottoms, reinforce some structural seams, etc. Nails are used to secure thin construction panels (such as cabinet backs), to reinforce corner joints of frames (such as angled frames) solid smooth doors).
Screws are used to fasten wood components (e.g. drawer fronts, cabinet backs, shelf runners), but primarily for fastening various types of hardware (hinges, locks, handles).
Pan nut screws are used, for example, to connect cabinet bottoms to cabinet sides and eyelet table legs.
- Screws are in demand in carpentry for detachable connections.
- It is screws that are increasingly used in connecting furniture fittings.
- Solid connecting screws confirmat are special screws for connecting cabinet parts and cabinets.
Connecting screws, consisting of two parts, are used to connect cabinet bodies to the structural assembly of door closers and door lifting mechanisms.
Combination screws and bolts are used to connect table legs to tabletops, legs to frames that form the base of bed furniture.
Summarize:
- Assembly with nails is faster and more convenient.
- The nail is more flexible, so if there is an excessive load on the cut, it bends, but “holds.”
- A nail is much less likely to cause cracks in the material.
- The nail is less susceptible to rusting and destruction due to corrosion.
- Nails are cheaper than high-quality self-tapping screws.
- Self-tapping screws are more resistant to pull-out loads.
- The screws can be unscrewed.
- In most cases, self-tapping screws require drilling.
- Working with a screwdriver is easier, but a nailer requires more skill.
When choosing between these two groups of fasteners, the most important factor is the type of load to which the connection is subjected.
When the force is applied to the fastener along its axis - to pull out - a self-tapping screw is the best choice, but in situations where the force is applied across the axis (to shear), a nail is the best choice.
Adhesive joints
Structural bonding refers to solid wood bonding, veneer bonding and assembly bonding.
The gluing technology consists of the following stages:
- Preparing the material for gluing;
- Preparation of adhesives and adhesive mixtures;
- Application of adhesives and adhesive mixtures;
- Gluing (pressing) wood plates in presses;
- Drying after gluing.
Areas of application:
- Structural gluing of softwood, hardwood and tropical wood;
- Surface gluing of “sandwiches” made of chipboard, fiberboard and MDF;
- Surface gluing of HPL/CPL films to chipboard, MDF;
- Forming patterns with marquetry-type veneer by gluing individual layers on top of each other;
- Gluing polystyrene foam.
Pressing parts
The curing process must take place under pressure to ensure sufficient contact of the bonded surface. The required pressure depends on the type and size of the part.
When laminating wood or adhesive joints, they can withstand a minimum pressing pressure of 0.6 MPa. The more intense the pressure curing, the higher the subsequent load-bearing capacity.
If we want to get wide sections of solid wood, we connect narrower pieces of wood side by side. Construction joints used to increase area may or may not be glued.
Non-glued expansion joints are used, for example, in cladding walls and ceilings, as well as in the production of non-glued components of wooden structures. Joining is a construction board made by gluing narrower pieces of coniferous or hardwood timber along the width.
Blanks can be glued:
- Butt joint: the joint is used for joints intended for frame panels, door frames, thresholds, frame infill;
- Profile joint: used for countertops, stairs, etc., i.e. where the joint is more intense and its high strength is required;
- Tongue and groove, for tongue and groove joints: the design is the same as for non-adhesive joints. It is used in the same way as a profile joint;
- On pins: pins strengthen the joint. They are used for wider workpieces.
Screws and self-tapping screws
Wood screws and self-tapping screws are convenient and practical fasteners to use. They provide reliability and strength to the connection of wooden parts and can be a worthy replacement for conventional nails.
Screw
- this is a fastening element, the rod of which is 2/3 covered with threads, and on the head there is a slot or a cross-shaped notch for a screwdriver. In order not to confuse a screw with a screw (which is practically not used in carpentry), remember that the screw has a tapered end. Self-tapping screws are very popular. When screwed in, they create a thread in the connection hole. Self-tapping screws, like simple screws, can be of different lengths and thicknesses, with different slots and head shapes, but on a self-tapping screw the thread is made along the entire length, right up to the head - this is their main visual difference.
Countersunk screws
are useful for connecting parts where the head should be flush with the surface or recessed inward, as well as for fastening fittings.
Countersunk head screws
most often used for attaching metal parts to wood (for example, corners for shelves) where design features allow this.
Round head screws
used for fastening sheet material, due to the thickness of which a countersunk head cannot be used, in places where the protruding head does not interfere with the design features or appearance of the product (for example, the back walls of cabinets).
Black screws
with a large pitch (distance between turns) of thread - these are the most common and cheapest self-tapping screws. They fasten drywall to profiles or wooden blocks, wood to wood, and are used for those jobs where appearance is not particularly important. The thickness of such screws depends on their length: the longer the screw, the larger its diameter. The hat is hidden, when fastened it becomes flush with wood or drywall. Disadvantages of black self-tapping screws: unattractive appearance and lack of coating, which causes the head to rust over time.
Yellow or white
with a protective coating - decorative screws, the thread runs along the entire length of the screw, the head is hidden. Sizes start with the smallest - 10-12 mm long and more. They are much more expensive than black ones, but they hold the material worse. They are used for finishing and decorative work, and for fastening with dowels in the wall. The hat does not rust and does not spoil the appearance.
Self-tapping wood grouse
- This is a very large self-tapping screw. It is used in places where there is a lot of pressure or load. The self-tapping screw has a hexagonal head. In order to secure it, you will need an open-end wrench or a screwdriver with a special bit head of the required size. It is necessary to drill out the wood for such screws, otherwise, due to its thickness, it will either not be possible to screw it into the tree, or the screw will split the wood.
Advice.
To make it easier to screw in the self-tapping screw, you can first dip it in machine oil
.
Screws and self-tapping screws for chipboard
made of hardened steel, with a countersunk head. Used in the same way as universal fasteners. For large diameters you need a guide hole; small screws can be screwed in without it.
Frame screws and self-tapping screws
made of hardened steel with a large thread pitch are needed, among other things, for screwing chipboard into the edge (side of the board), since they do not split chipboard and relatively thin wood. To make work easier, you can pre-drill guide holes for them.
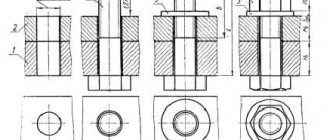
Connecting pins
Connecting with pins is one of the most common methods of connecting structures in furniture production. The pins are made from hard wood, mainly beech.
Glue is applied to the drilled hole. To ensure the surfaces fit tightly, the pin holes on each side should be 1mm deeper than the length of the pin. The diameter of the pin is selected depending on the thickness of the materials being joined.
The workpieces are connected in tongue and groove, they can also be connected with a half-groove. A technological joint is also left deep in the groove. The tongue-and-groove joint is less dense than the toothed joint. It is used in the production of drawers, shelves or door frames.
What are fasteners - dowels?
Dowels are rods of square, triangular or cylindrical cross-section, designed to secure two logs or beams in a log house to each other (lower and upper). The dowels are installed in the log house in a checkerboard pattern, the distance between them must be at least 1 meter. To begin with, a hole is drilled in the logs or beams, and then it is necessary to hammer the dowels into them. In this case, you need to use only wooden hammers so as not to damage the end of the dowel. The dowels are installed strictly vertically, so they will not prevent the logs or beams from sliding down. If the dowel is difficult to drive, then you should not be zealous; it is better to drill this hole with a slightly larger diameter.
These fasteners provide the log walls with stability and strength. Dowels during the shrinkage of the log house prevent deformation of the logs, reducing the likelihood of large cracks forming on them. Also, after the logs have dried, the dowels allow them to slide smoothly downwards, thereby reducing the gaps between the crowns of the log house. They are made in various sizes. Most often they are found with a diameter of 25-30 mm. The dowels differ not only in their sizes, but also in their varieties.
Frame joints
We divide the frame connections according to their location in the frame into corner and central.
Corner joints are created by connecting the ends of friezes around the perimeter. The ends of the friezes can be joined together:
- At right angles;
- On the pin;
- On the pin and groove;
- By overlap.
Central joints are used when connecting partitions to peripheral friezes of the frame or when connecting partitions to each other.
The most common are recessed pins, pins, and center slabs (for large pieces of timber structures).
How to choose the right dowel for assembling a log house?
When buying dowels for assembling a wooden house, you must consider the following:
- It is still advisable to purchase wooden dowels. The most durable are dowels made from birch. You can also purchase dowels made from oak, but they are too expensive.
- It is advisable to buy dowels with a circular cross-section; it will be easier to prepare a hole in the crowns for them.
- Both short and long dowels can be found on sale. It is recommended to stick to long ones; they can be cut to the required length on the spot.
- When purchasing, be sure to pay attention to any defects. There should be a minimum of them; it is advisable to purchase dowels that are perfectly smooth and without knots.
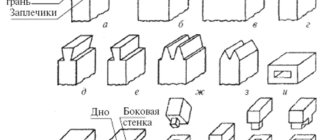
Tooth connection
The most common method of joining flat parts is the tooth joint, but crimp joints and, to a lesser extent, tongue and groove joints are also used.
The tooth joint is one of the oldest joinery knots. Precisely crafted teeth serve as a decorative element. The teeth are self-locking connections and do not need to be tightened into the jig during connection. Based on the shape of the teeth, we distinguish between dovetail and straight inserts.
What is a dowel
If you are interested in a dowel, what it is, you should find out. Translated from German, this word means “nail”, but it is not typical. The product is a pin that can have a round or square cross-section. The fastener has neither a head nor a point. It is smooth, and threads in some connections are completely undesirable. The length can be 150 mm maximum. But the sizes are not regulated in practice.
If you want to purchase dowels, what they are, you should know. This information also includes the material at the base of the products. This is usually metal or wood. The latter option is more common, because it is used for the construction of wooden buildings. The main goal that builders are trying to achieve when installing wood dowels is to resist shear.
Boards, logs and beams change size when exposed to external factors such as humidity and temperature. This happens disproportionately, which depends on the direction of the fibers. Parts move in different directions during operation. If you use a pin holding them, a rotation will occur due to the creasing of the material.