Fire retardant composition for a wooden house
Today, the Russian chemical industry offers many different fire-fighting compounds. Choosing a quality product among this abundance is quite difficult. Experts in the field of wood fire protection recommend using impregnations from the Pirilax series , developed by. These compositions are characterized positively by professionals and are currently one of the most effective fire protection products on the market. The Pirilax composition effectively prevents wood fire[2]. In addition, these compositions are safe for animals and people.
Fire retardant compounds for wood "Pirilax" contain non-washable antiseptics, which at the same time allows you to preserve the beauty of the wood and improve the performance characteristics of the wooden structure.
Methods of protection against rotting
Temperature changes, precipitation, and solar radiation lead to untimely rotting of wood. The first signs of decay are the appearance of mold and mildew. Large areas indicate that the material can no longer be saved. If wooden products or buildings experience atmospheric disturbances, high humidity from precipitation and condensation, it would not be a bad idea to carry out preventive work that will protect the wood from rotting.
The best helpers in this matter are antiseptics, which are pastes or liquid solutions. Some of them are universal, that is, they protect the material not only from moldy fungi, but also from beetles. Examples of such compositions are two popular products.
PINOTEX IMPRA is used for treating wooden surfaces that are not subject to further decoration. Usually these are beams, roofing straps, sheathing parts, that is, hidden parts of buildings. The impregnation is green. The appearance of mold, blue stains, fungus and rot is excluded on wood coated with it.
Recent Entries
Lilac perennials that are beautiful, compact and do not crowd out other plants Why when buying seedlings you should not take the sellers’ word for it and how to determine the age of the plant using 3 signs Tomato seedlings have turned purple or whitish: why the color has changed and how to save the plants
Antiseptic Pinotex Impra goes on sale in large-volume containers. Product price: 3 l – 1100 rubles, 10 l – 3350 rubles
Senezh Ecobio is used both as an independent coating and as a primer for varnish or paint. 2-3 layers of the product protect wood from rotting for 30 years.
If the wooden surface was originally treated with varnish, paint, drying oil or other water-repellent agents, SENEZH ECOBIO is useless
Treating wood with a fire retardant compound
The compositions should be applied to clean, unpainted wood using a brush, roller or spray. After impregnation, the wood should not be subjected to mechanical processing, as this will lead to a loss of protective properties. Attention! Treatment of prepared wood with the selected fire-retardant (fire-bioprotective) composition must be carried out in strict accordance with the instructions!
The tree will be reliably protected from fire after a single treatment with Pirilax at a consumption of 280 g/m2. Fire protection work with Pirilax impregnations can be carried out at low temperatures down to -25°C. To do this, the composition must be heated to 50-60°C or diluted with hot water in a ratio of 1 kg of impregnation per 0.5 kg of water[3].
- Federal Law No. 123-FZ “Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements”
- Biopyren "Pirilax" characteristics and description
- Features of the use of biopyrene "Pirilax"
How to protect wood from moisture?
If the moisture content of the material exceeds 15%, the structure of the wood begins to collapse: swell, delaminate, and then shrink. As a result, the products change their shape, cracks and gaps appear. Almost all wooden elements are susceptible to high humidity, with the exception, perhaps, of sisal and rattan, since they come from the tropics.
The experiment showed that water does not penetrate the pores of a block treated with a water-repellent composition, while it is quickly absorbed into unprotected wood
There are special solutions that protect wood from moisture. They are divided into two groups:
- penetrating;
- film-forming.
The first group provides a more reliable barrier against the penetration of liquid into the wood structure. The process of treatment with compounds of the second group must be repeated over time. Let's look at two products that resist high humidity.
Aidol Langzeit-Lasur is a medium-viscosity impregnating composition, excellent for covering house walls, country furniture, balcony and terrace railings, and fences. The azure is so safe that it can be used to cover children's toys and buildings. It has many decorative shades: silver-gray, teak, ebony, dark oak.
If coniferous wood is treated with Aidol Langzeit-Lasur, it must first be primed. This rule also applies to products damaged by fungus or mold.
Belinka Interier Sauna contains acrylic resins, water and additives. This is a colorless glaze, ideal for processing wood in baths or saunas. Two layers of the solution are applied with a roller, brush or spray.
Belinka Interier Sauna does not mask the natural texture of wood, but only makes it more silky and shiny. A 2.5 liter jar of azure costs 950-1000 rubles
Facilities
First of all, these are proven over decades of use in the USSR/RF, but are still successfully used, including simply under other names:
- The fire retardant composition for surface impregnation is “MS”, for deep impregnation – “MS 1:1”.
- For surface – “PP”, as well as “VIM-1”, “BANN 1”.
- The general composition of all is approximately the same - various salts, mostly “dual-use”, since their “main job” is mineral fertilizers + various industrial surfactants used for better adhesion/penetration into wood, as well as dyes.
A little later, during perestroika and after it, a huge number of new trains appeared. Not only industrial companies that traditionally produced paint and varnish products, but also companies that set the goal of becoming leaders in the new market of fire retardant materials began to engage in scientific development and implementation with lively advertising.
Thus, names appeared that were familiar to almost everyone who was involved in fire protection work. At least in your home/dacha for treatment, for example, a bathhouse, which was fashionable at one time; and many protective agents for this purpose successfully combined, at least at the level of advertising of finished products, not only the fight against fire, but also against mold, rot, aging/darkening, and insect pests of wood; improved, tinted, painted in colors that are pleasing to the tired eyes of the buyer/owner. Here are some of them:
- "KSD";
- "Attik";
- "Pirilax";
- "Old Elm";
- "OZK-45D";
- "Claude-01";
- “Pyrex”, “Ograx” and dozens of other brands of fire retardant compounds, including varnishes, paints, coatings, enamels, it’s impossible to list everything, because as soon as they were not named by manufacturers, they often had a recipe that was not much different from the good old “MS” and "PP".
An interesting detail: developed for a huge country with its distances, compositions under the brand “made in the USSR” were produced in dry form in bags, anticipating the advertising slogan “just add water” by decades, but new ones mainly appeared in the form of aqueous solutions in plastic containers from 1 l. Why this was done - no explanation needed.
At one time, fire-retardant paint and varnish products even poured into the Russian market from abroad from the famous concerns of our sworn friends. But their happiness was short-lived, since the declared “fabulous” quality, in fact, was not much different from domestic goods, and the cost was too high for mass consumption, for example, in construction. Today their market share is completely negligible.
It should be noted that wood antiseptics and fire protection by themselves, as a rule, do not add. With the exception of recipes/mixtures of substances specially developed by chemical scientists, called fire-retardant compositions/coatings, which must be indicated both in the technical data for commercial products and in advertising materials about them.
how much are ebony sex doll?
For all its advantages, untreated wood is not a durable building material. In order for a house, fence, gazebo, garden furniture and other elements of both the building itself and the suburban area to last a long time, wood requires reliable protection.
Ways to protect wood
Wood structures and parts have long been in demand in construction due to their environmental friendliness, manufacturability and mechanical strength. Today almost no house can do without wooden elements: rafter systems, floor beams, internal partitions, stairs and balustrades - all this is most often made of wood. But this material has enemies - fire, mold, fungi, insects and ultraviolet radiation. To protect wood from such negative factors, both constructive methods (correct placement, layout and operation of products and buildings) and special chemicals are used - therapeutic and prophylactic (antiseptics), protective and decorative (impregnations, glazes, varnishes) and fire-fighting (fire retardants) ). The best option is a combination of several methods of protecting wood for one structure, plus regular monitoring of its condition and periodic renewal of the outer covering (on average, such procedures are carried out every 4-5 years). In any case, prevention will be much cheaper than restoring an already damaged element.
Related video:
How to choose fire protection or bioprotection for wood?
When choosing fire and bioprotective agents for wood, you should follow special recommendations and carefully study the information on the product packaging.
- Manufacturer . Wood preservative is a rather complex product, and only a well-equipped enterprise with a long production history can produce it with high quality. Therefore, products of dubious and little-known origin should not be trusted.
- Coating service life . If a manufacturer claims that their product provides a protective layer that will last 2.3 years or 5 years, then this is most likely true. But when it comes to 20-40 years, it is better to refrain from buying. Only the most attentive buyers will pay attention to the fact that under this phrase, as a rule, there is a footnote where it can be written, for example, that such a period of protection is possible provided that the solution is applied by deep impregnation or soaking. Both of them are industrial methods, unattainable in everyday conditions. Another version of the so-called marketing ploy is that the manufacturer, under the promised long life in small print, writes that such durability is achieved provided that the composition does not wash out of the wood, which is impossible in principle.
- Composition consumption . As a rule, the cheaper the impregnation, the higher the consumption declared by the manufacturer. Therefore, when you see a seemingly inexpensive product on a store shelf, you should not rush to buy it. To begin with, it is better to calculate how much impregnation will be required to solve a specific problem, subject to the manufacturer’s recommendations for consumption. The average consumption rate should not exceed 200-250 g/m2. And on some products you can find figures of 500-600 g/m2, which is quite typical for fire-retardant materials, but cannot in any way be the norm for bioprotective compounds.
- Versatility . When choosing a complex bio-/fire retardant agent, you need to take into account that some manufacturers deliberately combine the functions of antiseptic and fire retardant actions, speaking of their mutual reinforcement. But experts say that even seemingly compatible compounds in a solution may not only fail to provide a positive effect of enhancing each other, but also reduce the bio-/fire-retardant properties. It is better to purchase specialized tools for solving different problems separately.
- Availability of a certificate . All fire retardant compounds and materials must have a certificate of conformity and a conclusion from the sanitary-epidemiological station. Without these documents, the sale of fire retardant products on the territory of Ukraine is prohibited. Require the presentation of appropriate confirmation at points of sale!
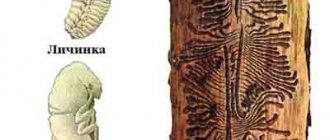
Bioprotection - protection of wood from rotting and insects
Constant wetting of the surface and the accumulation of condensation on it lead to the formation of fungi and mold, and the appearance of rot. And wood is much more difficult to withstand the effects of dampness than all other building materials. Moisture can destroy wood cells, cause decomposition and splitting of structures. If the process is not prevented or stopped in a timely manner, then in a few months the rot will “eat through” the tree. As a result, the beam or truss structure will collapse, pulling other building and finishing materials with it. Their bioprotective treatment will help to avoid such consequences.
Raw material selection
You need to take care of protecting wood from rotting even at the stage of purchasing and storing timber and lumber. In production conditions, wood harvesting goes through several stages: cutting, treatment with a preservative composition, drying for a year, sawing. Technological violations at least at one of the stages lead to the appearance of harmful bacteria and insect larvae in the material.
In any case, when choosing wood, it is useful to know that different species have different resistance to rot. Hardy trees include pine, ash, cedar, larch and oak, medium hardy trees include spruce, fir and beech, and low hardy trees include birch, elm, hornbeam and maple. If defects were discovered after the purchase of the material, it must be treated with an antiseptic before storage, including “healthy” products for prevention.
It is difficult to determine the condition of a tree by eye. Of course, it is necessary to screen out wood with obvious signs of waterlogging: for example, if the board has a helical shape (distortion of the cross section), there is blue discoloration or small pockets of mold. But only a person with extensive experience in the specialized field (for example, a carpenter) will be able to indicate a moistened product - by the presence of cracks in the end, barely noticeable warping of the material, and the approximate weight of workpieces of common types. An inexperienced person will determine this only during processing. Signs of very wet wood - the shavings removed with a plane are easily crushed, and the shavings from the cross use of the chisel crumble.
The standards contain more precise requirements for the moisture content of wood materials used for certain needs:
- construction of walls and fences - 6-20%;
- installation of rafter structures and laying of beams - 9-15%;
- installation of window and internal door units - 6-12%;
- installation of external door frames - 9-15%;
- creation of interior finishing parts - 9-15%',
- manufacturing of platbands and external cladding - 12-18%.
It is important to take into account that the humidity of small parts and connecting elements should be 2-3% lower than that of the main product in which they are used.
Assortment classification
Impregnations, disinfectant and antifungal solutions, etc. are used as special antiseptic agents. The choice of composition is determined by the designated task and the property of the necessary protection. It should be taken into account that different types of wood absorb drugs differently, and the consumption of the product depends on this. Thus, pine, birch and beech wood have good absorption; cedar, larch, hornbeam, oak, maple, linden, alder and aspen have moderate absorption; spruce and fir have low absorption.
Insecticidal impregnations that destroy insect larvae and prevent their appearance have an “ambulance” effect. Such preparations are made on a water or alkyd basis. The former serve mainly for temporary (annual) conservation of wood for the period of harvesting, transportation and storage. Alkyd-based antiseptics work much longer. They create coatings that are resistant to fading in the sun and do not absorb water, and are also suitable not only for medicinal purposes, but also for preventive treatment.
Preparations intended to combat fungal diseases of wood (mold, blue, brown and brown rot) contain special substances in their formulation - fungicides. Fungicidal solutions are made based on water or white spirit. Solutions of the first group are environmentally friendly, inexpensive, but are washed out with water over time, so it is better not to use them for treating elements that are in direct contact with the soil and moisture. Preparations based on white spirit penetrate deeper into the wood, are not washed out with water, but are less environmentally friendly (they have a strong, specific odor that complicates the processing process).
Well, if the wood has been subjected to fungal infection, the entire surface is thoroughly cleaned and special disinfectants with a high content of active substances are used, including those that can bleach wood that has changed its color.
Transparent "cosmetics"
Lazuries and varnishes not only protect wood from ultraviolet rays and precipitation, but also give it an attractive decorative effect.
Varnishes intended for interior use are environmentally friendly and are characterized by increased resistance of the finished coating to abrasion and moisture. Varnishes for external use, made on an organic basis, create an elastic coating of increased strength that protects wood from temperature and humidity atmospheric fluctuations and exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Lazuries (glazing compounds), being transparent, leave the wood texture visible. They serve to protect and decorate new, previously unpainted surfaces. Compared to paints, the protective effect of glazes is much higher. Firstly, the content of coloring pigments in them is minimal, which ensures good absorption into wood, and secondly, they contain many more special additives that prevent rotting of the material. For long-term use in atmospheric conditions, dark-colored glazes are more suitable: they better mask the graying of wood, and their service life is on average 3-4 years (for light glazes - 2-3 years).
Fire protection - protecting wood from fire
In a dry state, wood ignites and spreads fire, at a temperature of 200-250 ° C it chars, and at 300 ° C it begins to collapse. We should also not forget that construction products and materials can release toxic products during combustion that are hazardous to human health. Therefore, it is very important to limit the time of exposure to fire on the structural elements of the building. To combat the low fire resistance of wood, special fire retardant compounds are used - fire retardants, which reduce the flammability of the material and protect its surface from the spread of flame.
Theory and practice
Wood has an interesting quality: the larger the cross-section of a wooden structure, the more difficult it is to ignite, and when burning, coal is formed on the surface, smoldering more slowly. Therefore, massive bars and logs retain their load-bearing capacity during a fire for quite a long time.
It is also worth noting that the heat reflectivity is higher for a wooden structure with a smooth surface, that is, it is more difficult to ignite. Any chips, protrusions and cracks increase the likelihood of fire.
If you are building a completely wooden house, fire retardant treatment will be required for all structures, including external walls.
In a house made of other materials, wood, which is used in the attic floor and roof structure, requires priority attention, since their collapse is dangerous to human life and can lead to an increase in the area and intensity of the fire. Fire-retardant treatment of wooden surfaces in places of normal and emergency evacuation is also necessary - entrance areas, terraces, first floor balconies, stairs, etc. In addition, attention should be paid to places where there is an increased risk of fire - around sockets, near the fireplace, etc. d.
To protect wood from fire, constructive measures are also used, such as increasing the cross-sections of the most loaded wooden elements, removing wooden structures from fire sources or creating fireproof cladding, etc.
Assortment classification
For wood processing, two groups of fire-retardant materials are used, which are divided depending on the methods of their application - impregnation and coating.
- Fire retardant impregnations are solutions of phosphoric or boric acid salts, most often water-soluble. Under their protection, wood chars at the point of contact with fire, and the structure as a whole resists fire for a long period and prevents the spread of flame.
- Fire retardant coatings are paints and varnishes that create a thin heat-reflecting layer on the surface of wood. When exposed to high temperatures, it swells, forming a heat shield of solid non-flammable foam (similar to the action of a fire extinguisher), which prevents ignition and the spread of flame over the surface and slows down charring.
It is better when wood is treated with fire retardants in an industrial environment. In this case, the drug under pressure penetrates as deeply as possible into the wood, so this fire protection is more durable. When purchasing untreated material or when the initial treatment has expired, you will have to solve the problem yourself. Apply the protective agent using a brush or spray gun only to a clean, dry surface.
Compliance principles
When independently choosing a fire retardant for wooden structures at home, you should take into account its effectiveness indicators. So, all funds are divided into three groups. The compositions of the first group, according to test results after two minutes of exposure to a gas burner flame, allow a mass loss of a wood sample of no more than 9% and ensure the production of a wooden structure with flammability class G1, the second - a mass loss of 9-25% and flammability class G2. Products of the third group do not provide adequate fire protection for wood, so they are not worth buying. It is also better not to buy compounds whose effectiveness has not been indicated by the manufacturer.
For processing wooden rafters and finishing stairs, materials with flammability class G1 are used; for all other cases, products of class G2 are sufficient. Information about the level of fire retardant effectiveness must be indicated on the packaging.