Watching this or that tree growing in the garden or walking in a forest among green spaces, we rarely think about their age. But some tree species can outlive humans for several generations.
Marvelous? Yes, that's Mother Nature. Having created favorable conditions for development for its “brainchildren,” it is not without reason that it creates one species at one end of the planet, and a completely different one at the other. After all, the lifespan of representatives of the plant world, including trees, directly depends on their habitat, that is, on whether it is related or whether it is necessary to adapt to it.
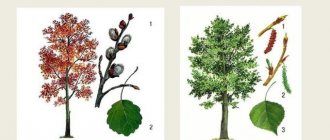
How many years do oak and birch trees live?
Many people who love to relax in nature, walk through the forest or just sit in the park, pay attention to the huge, tall trees. The most common question that arises is how many years trees live. Some of the most beautiful and mysterious are oak and birch groves. Walking past massive oaks or slender and tall birches, do you think how many years do trees live?
Mysterious oak
Walking through the oak grove, you pay attention to the mystery of these trees. The question involuntarily arises in your head about how many years an oak tree lives. It is one of the common trees in the northern hemisphere and belongs to the Beech family. There are legends about this mighty tree. Even in ancient Greece, oak groves were called the habitat of the goddess of fertility Demeter and the beneficial properties of oak were noted.
For example, oak bark has astringent and anti-inflammatory properties and is used in folk medicine. Oak fruits - acorns - are rich in such a useful substance as quercetin, and are used to relieve swelling, inflammation, spasms, and also have excellent antioxidant properties. Oak is a very durable material, which is why it is used in the manufacture of household furniture, wine barrels and various artistic items. Oak, like many other trees, has its own types. In total there are about 600 species of oaks. The most common are petiolate, jagged and rocky. Regardless of the type, the tree can reach a height of 20 to 40 meters, and the trunk circumference can be up to 9 meters.
How many years does an oak tree live?
Walking past old oak trees, you wonder how many years do trees with such powerful trunks live? The average lifespan of an oak tree does not depend on the type of tree and is 300 - 400 years. But there are rare cases where trees live up to 2000 years. For example, the Mamre oak, located in Palestine, is about 1900 years old. Christians consider it a holy tree. According to the Bible, Patriarch Abraham received God under this tree. The Stelmuz oak grows in Lithuania; it is considered the oldest oak tree in Europe; according to some sources, its age is 2000 years.
Beautiful birch
Besides oak, one of the most common trees in the northern hemisphere is birch. It belongs to the deciduous genus, the Birch family. It occupies one of the first places in beauty; its graceful white trunk attracts with its stream of emanating light. Birch occupies a special place in the culture of Slavic, Finnish and Scandinavian ancient tribes. For example, among the Slavs this tree protects and protects from evil spirits. Birch is famous not only for its beauty, but also for its benefits and healing properties. Birch sap, which is collected in early spring, has a large amount of minerals and is beneficial for humans. Birch buds contain a large amount of essential oil, so they are used as a diaphoretic and blood purifier. Birch is the main raw material for producing charcoal, which is used in everyday life; in addition, durable wood is obtained from birch. In total, about 120 species of birch trees are known. The most common is downy birch; in addition, yellow and weeping birch are often found. These species reach an average of 25 - 30 meters in height and up to 80 centimeters in diameter. Walking through a birch grove and admiring such beauties, you inevitably wonder how many years trees live?
How many years do birch trees live?
This type of tree grows in almost all regions of the northern hemisphere, and therefore it is important to know how many years the trees live. Birch, unlike oak, lives as long as it is prescribed by a certain species. The average life expectancy of a fluffy and weeping species is approximately 100 years. In turn, the life period of yellow birch reaches 150 years.
fb.ru
Distinctive features of red oak
Most often found on river banks. Does not like stagnant water in the soil. North America, in particular Canada, is considered the birthplace of red oak. Such trees reach a height of 25 meters. Externally, the trunk is slender and smooth. The gray bark darkens and cracks over time. The oak crown is tent-shaped, green with yellowish tints closer to the ground. The leaves are large, sometimes their diameter reaches 25 cm. They have pointed blades. In autumn they turn red and fall off.
The fruits are small, spherical, no more than 2 cm in size. Ripe acorns are red, slightly brown. They ripen by the end of autumn; the first year is a poor harvest. Sustainable fruitfulness – up to 20 years. The tree is frost-resistant, calmly withstands strong winds and bright sun.
How many years does a birch tree live?
Birch has long been considered the most favorite tree of poets, artists and ordinary people. They wrote poems about it, sang songs, painted it, and used it in medicine. This is a beautiful tree with interesting colors, tasty sap and medicinal pollen. Throughout its life, people use healing branches, leaves, buds, and bark. It seems to people that the birch tree lives forever.
Birch. Types and lifespan
There are about 120 species of birch, 64 species are found in the forests of Russia. The average lifespan of a birch is about one hundred years and depends on living conditions. In principle, this is an unpretentious tree that can live well in any soil. The main thing is that the soil is moist, since birch loves water and consumes up to 250 liters per day.
In Russian forests, birches live no more than 120 years, with the exception of iron birch, whose lifespan is almost 400 years.
Just 100 years ago, birch was a rarer tree than it is now. It grew mainly along river banks and in forests where coniferous trees had fallen. So she grew up in different places of the taiga. For more than 150 years, the birch tree did not stay in one place.
Birch also has permanent habitats. On the border of the forest near the Arctic Circle there grows twisted birch, in the Pamirs - Pamir birch with pink bark, in the Caucasus - Radde birch, also with pink bark, in Transbaikalia - black birch with shaggy bark.
Stone birch grows in the Far East. Its age is 3-4 times greater than white birch and is 500 years old. Its trunk is more like an apple tree, the only difference is in the bark. The color of the bark is neither like a birch nor an apple tree. This is a pink-gray bark that lags behind the tree itself and hangs down in long strips.
Warty birch or silver birch are widespread. She grows quite quickly, starting from the age of 10, she grows by 75-90 cm per year and lives 50-60 years.
Application in medicine
In folk medicine, they use everything that birch can provide. Its juice is an excellent immunostimulating, cleansing and vitamin remedy. Bath brooms are made from branches and leaves, which, under the influence of hot air in the bath, release essential healing oils that have a beneficial effect on the condition of the skin and the entire human body.
Birch buds help well with many diseases, because they contain essential oils, tannins, resins, grape sugar, flavonoids and ascorbic acid. It is a good antiseptic and expectorant that is used to treat diseases of the respiratory system. In addition, they are used in the form of lotions or dressings for various soft tissue wounds.
Birch sap is recommended for use in cases of poisoning and cancer. It perfectly stimulates metabolism, has a diuretic and anthelmintic effect.
Birch leaves have a bactericidal effect and help cope with headaches, rheumatism, and nervous system disorders. Decoctions and infusions are used in the treatment of the upper respiratory tract, arthritis, gynecology and dermatovenerology.
These are not all the diseases that birch treats.
Grow a birch tree yourself
Any gardener dreams of having a long-lived birch tree on his plot. It is not difficult to grow. Seedlings can be purchased ready-made, preferably with a ball of earth on the roots.
Dig a fairly deep hole and add a mixture of garden soil, humus, sand and peat.
If planting occurs in the spring, you can add a complex fertilizer, in the fall - phosphorus-potassium fertilizer in the amount of 200 grams. The distance between seedlings should be at least 4 meters, since the birch root system is actively developing and requires a lot of space.
You can grow birch from seeds, which are sown in shallow holes and covered with a layer of humus. Before planting, they must be kept in the cold for a month, then dried at room temperature. Seeds are sown at the beginning of winter in already frozen soil or in early spring, immediately after the snow melts.
When growing this healing tree, it is important to pay attention to the control of weeds that can interfere with the development of the plant. You need to weed the soil regularly, but not deeper than 3 cm, so as not to damage the roots. In order to prevent fungi and various pests, the tree crown must be sprayed with fungicides and insecticidal preparations every year.
To form a beautiful tree shape, it is recommended to prune the branches annually. This is done in early spring before birch sap begins to secrete.
By growing a birch tree on your property, you will be able to enjoy its healing properties throughout your life. It will become an indispensable assistant in the fight against many diseases. Thanks to its impressive life expectancy, birch will be useful for more than one generation.
MegaOgorod.com
How to determine the age of an apple tree?
Sometimes gardeners buy a plot with trees growing on it. How to determine the age of the apple tree in this case? After all, maybe it is already so old that soon it will not bear fruit at all, and there is no point in feeding it and other measures related to increasing productivity. The most well-known method is to determine age by rings on a tree cut. But in the case of fruit trees, it will not work - because in this case they will simply die.
Pressler's drill
Using a Pressler drill, you can drill out a fragment of a tree with virtually no harm to it in order to determine its age. By looking at the rings, you can learn not only about the age of the apple tree, but also about the conditions in which it grew. If the size of the rings is wide, it means that the plant was well cared for and the climatic conditions were favorable. Narrow rings indicate periods of drought, attacks by harmful insects, excessive harvests and other negative factors. When counting, you need to distinguish between real and false rings. The former form a closed circle, the latter do not.
You can determine the age of an apple tree by cutting down the oldest branch on it. You need to add two years to these rings - this will be the age of the seedling.
You can look at the rings on the cut of an old tree branch to determine the age of the apple tree.
How many years do birch, rowan, linden, oak live?
Moonlight Sonata
Rowan grows quickly for the first 15-20 years, bears fruit annually from 8-10 years of age, lives up to 100 years, although some trees live up to 200 years. Among the trees of our forests, linden lives for a very long time: on average up to 300-400 years, and some individuals live up to 1200 years. Oak lives up to 800 years, birch only about 100 years. The maximum age of most birches does not exceed 100-120 years, for yellow birch - 150 years, some trees reach 300 years.
https://uvaga.biz/ryabina/glava_i_vse_o_ryabine https://www.woodmagic.ru/chernolesie/lipa/ https://poznaimir.hut1.ru/derevo.html [link blocked by decision of the project administration] https:// flower.onego.ru/kustar/betula.html
Eugenio
birch 100-150 years old, rowan 80-100, linden - 300-400, oak up to 1500
KOMOV MIKHAIL
Birch lives 150 years, rowan - 100, linden - 300-400, oak - 1000-2000
Emilia Gadzhieva
birch lives 100-150 years but can live up to 300 years
Lyudmila Choban
Rowan grows quickly for the first 15-20 years, bears fruit annually from 8-10 years of age, lives up to 100 years, although some trees live up to 200 years. Among the trees of our forests, linden lives for a very long time: on average up to 300-400 years, and some individuals live up to 1200 years. Oak lives up to 800 years, birch only about 100 years. The maximum age of most birches does not exceed 100-120 years, for yellow birch - 150 years, some trees reach 300 years.
Lyudmila Dementieva
birch lives 100 years
Artyom Lelikov
I do not know
Kirill Karpov
thanks for the answers, I will find them all useful
Criticism of arguments - questions for alternative history
What were railroads and wooden buildings made of?
If about 200 years ago all the forests were destroyed, then what were railroad ties, buildings, ships, and stoves made of then? My relatives live in the Oryol region - a region not rich in forests, so they have practically no wooden buildings!
Fiction and painting
What about the mention of forests and logging in literature and paintings of the 18th and 19th centuries? Just ignore? Or were these masterpieces created by order of the secret world government in order to erase these events from people's memory? Seriously? Damn it, this theory is so crazy that it’s hard to find words from amazement: global catastrophes, nuclear war - and no traces of these events, except for “young forests” and “soil-covered” first floors of houses...
Which tree has the longest lifespan on Earth?
Valera peace Yao
The oldest tree Long-lived pine (Pinus longaeva) USA, Eastern Nevada 5100 years
Records in the plant kingdom https://www.calc.ru/278.html The oldest oak in Europe is Stemluzhsky. It grows in Lithuania. The oldest trees on Earth are pines (the age of long-lasting or bristlecone pine (Pinis longaeva or Pinis aristata) in California is approximately 4900 years old; other sources are about 6000 years old); such species do not grow in Europe. https://kraj.vitebsk.net/?page=guarding&sod=03 Modern scientists discuss about 300 hypotheses of aging, but they fit well into three main directions. The first group of hypotheses suggests that aging and death are a process inherent in the genome. Obsolete individuals must inevitably give way (space, resources) to their young descendants. Therefore, Nature took care of the continuity of life by placing a special aging program in the genes, that is, an order for self-destruction. The reality of the aging program is confirmed by the existence of a limiting number of cell divisions (Hayflick limit), and the discovery of the telomerase cell division counter. However, P. Yu. Zhmylev reports that plants are unlikely to provide much evidence to support such a programmed cell division counter. At the same time, genes responsible for leaf aging have been found in some plants. The genes for leaf senescence in annual plants, such as sorghum, are located close to the genes for flowering, so it is logical to assume that flowering inevitably entails senescence. This connection, however, is not so unambiguous, since about 30 leaf senescence genes are currently known, which represent a complex regulatory network. And flowering itself is regulated by a significant number of genes and may be completely unrelated to aging, as is typical for rice. Apparently, plants do not have a universal genetic apparatus for longevity. https://elementy.ru/news/430379 Time of life. Some species of Conifers are among the longest-living plants in the world. ——For example, the mammoth tree is such a long-liver; the age of some of its specimens is more than 3000 years, but the longevity record is broken by another species, namely the North American long-lived pine (Pinus longaeva). ——A specimen of this species was found in Eastern Nevada, whose age is estimated at approximately 4900 years, that is, almost five thousand years. This means that already during the construction of the Cheops pyramid this plant was already quite old (it was more than 200 years old). https://www.krugosvet.ru/articles/116/1011696/1011696a2.htm The oldest - The oldest existing species is ginkgo biloba, which lived in the Jurassic period, 160 million years ago. —-The long-lived pine lived the longest - 5100 years - in Nevada (USA). —-The oldest living tree belongs to the same species and grows in the White Mountains of California. This pine is called "Methuselah". It is believed to be about 4600 years old. https://e-lib.gasu.ru/eposobia/botany/00/02/more01.htm FROM THE GUINNESS BOOK OF RECORDS
Ruslan
American sequoia up to 1000 years old and the tallest
Vasabi
I don’t know for sure... but maybe oak?
Nana
Sequoiadendron giant (mammoth tree).
Sequoiadendron giant, mammoth tree - This is a coniferous evergreen tree of gigantic size, native to North America. Once upon a time, 60 million years ago, it was widespread in the Northern Hemisphere, but is now preserved only in a special reserve in the Sierra Nevada mountains in California. The grove has only about 500 trees.
This is one of the tallest and longest-living trees on the globe. In their homeland, individual specimens reach gigantic sizes: 140 m in height and 20 m across the trunk, living up to 4–6 thousand years. Struck by its gigantic size and the peculiar arrangement of huge arched hanging branches reminiscent of mammoth tusks, the discoverers gave it the name mammoth tree.
This unusually majestic and monumental plant was given the names of famous personalities. So, in the USA it is called Washingtonia in honor of the first American president D. Washington, and in England - Wellingtonia in honor of the hero of the Battle of Waterloo, the English Duke of Wellington.
The wood has a reddish-pink color, for which it is also called “Sierra Redwood”. It does not rot and is used in construction to make tiles. The largest sequoiadendrons in the reserve have their own names: “Father of Forests”, “General Sherman”, “General Grant”. The Americans calculated that the General Sherman sequoiadendron contains about 1,500 cubic meters of wood, with a height of 83 m and a trunk diameter at the base of the tree of 11 m. To transport it would require a train of 20–25 cars. An orchestra and three dozen dancers sit freely on the stump of another tree. There are also known tunnels made in the lower part of the trunks, through which cars can freely pass.
Sequoiadendron was discovered by traveler Lobb in 1850, and already in 1858 several specimens were planted in the Nikitsky Garden. A beautiful crown in the form of a clear, regular pyramid, graceful needles and cones, rapid growth and size have made sequoiadendron attractive for the design of parks. Although its seeds have low germination, it propagates well by cuttings. In the Nikitsky Garden you can not only see the oldest and most majestic sequoiadendron trees on the southern coast of Crimea, but also visit a grove of 40-year-old trees obtained from cuttings and already reaching impressive sizes.
Ilnur Khamidullin
baobab
Julius
In America there, Muir Woods, is 70 meters high, 4.3 meters in diameter! They are the oldest trees on earth!!! !
The oldest trees in the world
Despite the fact that coniferous crops live longer than deciduous ones, real long-livers are found in all botanical types. Naturally, the usual apple tree, linden tree or maple tree cannot be included here, but amazing ancient giant trees are found all over the world (Figure 4).
Here are some of them:
- Methuselah Pine: This long-lived plant is found in California, USA. Scientists have determined that the pine tree is over 4,500 years old, but it is impossible to see it with your own eyes. The tree grows in a nature reserve, whose employees carefully conceal the secret of its location.
- Sequoia General Sherman: also grows in the USA, in Sequoia National Park in California. Its age is estimated at approximately 2500-2800 years. There are always a lot of tourists here, but it is noteworthy that the sequoia continues to grow: every year its trunk increases in girth by 1.5 cm.
- Tikko spruce: grows in Sweden. Scientists, using the method of radiocarbon analysis of the roots, have established that its age reaches 9.5 thousand years.
In general, amazing long-lived trees are found all over the world: cedars in Lebanon, cypress in Iran and even chestnut on the slope of Mount Etna in Sicily. The very fact that these plants managed to survive so many years and remain viable to this day is amazing.
Tree height growth rate
Typically, living things, including us, have a period of active growth when they are young, but as they age, growth slows down or stops altogether. The growth rate of trees in height has the same character. After a period of active growth in height, the growth rate of the tree decreases, and it begins to gain weight due to the trunk and side shoots. The figure shows the general nature of the relationship between the height of most trees and its age. The schedule is divided into three phases. 1 is the initial phase of slow growth, followed by a phase of rapid growth - 2. When the tree approaches a certain height, the growth rate drops - phase 3. Of course, time and height values will vary for each individual tree depending on the species and environmental conditions.
The general nature of the dependence of the height of most trees on age
Different types of trees grow at different rates. Depending on the growth rate, trees are usually divided into groups. In tables 1 and 2, trees are divided into groups depending on the tree's growth rate per year. Trees gain such growth rates during the active phase (between the ages of 10 and 30 years).
Very fast growing
Fast growing
Moderately growing
Table 2: Slow-growing trees
Slow growing
Very slow growing
growth 0.25-0.2 m
Siberian cedar pine
Dwarf forms of deciduous trees (Dwarf willows)
Dwarf forms of conifers (Obtuse cypress)
Knowledge base
| Name | Height, m | Life expectancy, years |
| Homemade plum | 6–12 | 15–60 |
| Gray alder | 15–20 (25)* | 50–70 (150) |
| Aspen | Up to 35 | 80–100 (150) |
| Mountain ash | 4–10 (15–20) | 80–100 (300) |
| Thuja occidentalis | 15–20 | More than 100 |
| Black alder | 30 (25) | 100–150 (300) |
| Birch warty | 20–30 (35) | 150 (300) |
| Smooth elm | 25–30 (35) | 150 (300–400) |
| Balsam fir | 15–25 | 150–200 |
| Siberian fir | Up to 30 (40) | 150–200 |
| Common ash | 25–35 (40) | 150–200 (350) |
| Apple tree wild | 10 (15) | Up to 200 |
| Common pear | Up to 20 (30) | 200 (300) |
| Rough elm | 25–30 (40) | Up to 300 |
| Norway spruce | 30–35 (60) | 300–400 (500) |
| Scots pine | 20–40 (45) | 300–400 (600) |
| Small-leaved linden | Up to 30 (40) | 300–400 (600) |
| Beech | 25–30 (50) | 400–500 |
| Siberian cedar pine | Up to 35 (40) | 400–500 |
| Prickly spruce | 30 (45) | 400–500 |
| European larch | 30–40 (50) | Up to 500 |
| Siberian larch | Up to 45 | Up to 500 (900) |
| Common juniper | 1–3 (12) | 500 (1 000) |
| Common falsesuga | Up to 100 | Up to 700 |
| European cedar pine | Up to 25 | Up to 1,000 |
| Yew berry | Up to 15 (20) | 1 000 (2 000–4 000) |
| English oak | 30–40 (50) | Up to 1,500 |
| Baobab | 18-25 | 1000 (5500) |
* The height and lifespan of trees in particularly favorable conditions are indicated in parentheses.
Return to main page | Changes in European land cover over the last 150,000 years | Taxonomic units | Classification of wildlife | Biological resources of plant origin | Classification of cultivated plants | Centers of origin of cultivated plants (according to N.I. Vavilov) | Biological resources of animal origin | Lifespan of some animals | Duration of gestation and number of cubs born at the same time | Maximum sizes of some vertebrates | Brain mass, g | Brain mass in relation to body mass, % | Flight speed of some birds and insects | Egg and body mass of birds | Bird flight distance | Number of wing beats in birds (per second) | Oxygen requirement of some organisms | Upper hearing limit, Hz | Body temperature and pulse rate | Mammal class | Species of animals and birds that became extinct in the recent past | List of fauna objects that have disappeared in Russia and are excluded from the Red Book of the Russian Federation (as of November 1, 1997) | Objects of world cultural and natural heritage in Russia | Natural monuments of federal significance (as of 2000) | National parks of the Russian Federation | State natural reserves of federal significance under the jurisdiction of the Russian Ministry of Agriculture | State natural reserves of federal significance administratively subordinate to the Ministry of Nature of Russia | The largest botanical gardens in Russia | Record-breaking plants | Wood Density | The greatest depth of root systems | Preservation of seeds' ability to germinate | Poisonous plants | Diploid set of chromosomes of cells of some organisms (2n) | Genetic code | A complete "dictionary" of the genetic code for amino acids
Description
Oak is a powerful deciduous or evergreen tree belonging to the beech family (genus of shrubs).
For natural growth, the plant requires a temperate climate, so most often it can be found in the Northern Hemisphere, sometimes in high mountain regions. Regardless of the species, all trees have common features. The height ranges from 35 to 50 m. Some specimens reach 60 m. The trunk is very thick, and its bark is rough and covered with deep cracks.
It’s remarkable what oak looks like in autumn. The usual green summer foliage changes to a “clothing” of red, purple, orange, brown, and yellow tones.
Wood reacts strongly to lighting. Its branches are sinuous because they stretch towards the light and change their direction depending on weather conditions.
As for the root system, it is as powerful and well developed as the above-ground part and goes deep into the soil. Giants prefer to grow in nutritious soils. In this case, the humidity should be moderate. But there are representatives who have chosen swampy or arid places.
Flowering occurs in late spring with the dissolution of small bisexual green flowers. Moreover, female flowers contain only a pistil, while male flowers (collected in inflorescences) contain only stamens. Pollination occurs with the participation of insects or wind.
After flowering, a fruit is formed - an acorn of different lengths with a cap, the so-called plus. The shape of the fruit and the appearance of the pluses determine the varietal identity of the oak.
When is it necessary to uproot old trees?
Despite the fact that coniferous crops live longer than deciduous ones, real long-livers are found in all botanical types. Naturally, the usual apple tree, linden tree or maple tree cannot be included here, but amazing ancient giant trees are found all over the world (Figure 4).
Here are some of them:
- Methuselah Pine: This long-lived plant is found in California, USA. Scientists have determined that the pine tree is over 4,500 years old, but it is impossible to see it with your own eyes. The tree grows in a nature reserve, whose employees carefully conceal the secret of its location.
- Sequoia General Sherman: also grows in the USA, in Sequoia National Park in California. Its age is estimated at approximately 2500-2800 years. There are always a lot of tourists here, but it is noteworthy that the sequoia continues to grow: every year its trunk increases in girth by 1.5 cm.
- Tikko spruce: grows in Sweden. Scientists, using the method of radiocarbon analysis of the roots, have established that its age reaches 9.5 thousand years.
Figure 4. The oldest trees in the world: 1 – Methuselah pine, 2 – General Sherman sequoia, 3 – Tikko
spruce Trees are the lungs of our planet, which is why it is so important to preserve green spaces as much as possible. Unfortunately, sooner or later any tree ages and dries out irrevocably, and it has to be uprooted
Of course, owners of private houses try to keep trees alive for as long as possible by carrying out anti-aging pruning and proper care. But, if these procedures do not help, it is better to cut down the old trunk and plant a new young tree instead.
Foresters do much the same thing: they cut down only completely dry trees, and annually replenish the green spaces with new specimens. This is the only way to preserve a green forest and get rid of possible problems in the form of diseases that old trees can cause.
Spreading
Culture is rarely found in the North, feeling most comfortable in areas from the Caucasus to the Urals, in Western Europe, Africa, and some Asian countries. Under natural conditions, the tree prefers to grow on the banks of reservoirs, as it loves moderate humidity, in places with fertile soil.
The crop grows best on moist loams, since on such soils the roots quickly grow both in depth and breadth. It is known that pedunculate oak is a broad-leaved tree, but it is very often found in mixed forests along with conifers. But sometimes you can admire a free-standing mighty tree.
If conditions are unsuitable, then the pedunculate oak tree slows down its development. In this case, the height reaches no more than 30 m.
Landing Features
You can grow mighty oak trees from seeds. Acorns should be sown in the fall or late spring after being stored in a cool, moist place. To do this, it is better to select a whole bed and make holes or furrows in it (as you prefer) with a depth of no more than 7 cm. The seedlings grow up to 12 cm in a few weeks. Acorns have an impressive supply of nutrients, which ensure intensive growth. If the conditions are favorable and care is provided, then after a year or two the young plants can then be transplanted to a permanent place.
It is best to plant pedunculate oak, the signs of which were discussed above, on fertile, non-acidic soils. Since the plant loves light, you need to choose a sunny, open place for it, but without drafts. The fact is that young seedlings can be seriously damaged by sudden gusts of wind or frost.
Notes
↑ show compact
- ↑ For the conventionality of indicating the class of dicotyledons as a superior taxon for the group of plants described in this article, see the “APG Systems” section of the article “Dicotyledons”.
- ↑ Neishtadt M.I. Identifier of plants in the middle zone of the European part of the USSR. Manual for secondary school. – M.: GUPI MP RSFSR, 1954. – P. 169-171. – 495 p.
- ↑ Go to: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Gubanov I. A. et al. Wild useful plants of the USSR / resp. ed. T. A. Rabotnov. – M.: Mysl, 1976. – P. 95-97. – 360 s. – (Reference books for geographers and travelers).
- ↑ Serbin A.G. et al. Medical botany. Textbook for university students. – Kharkov: NUPh Publishing House: Golden Pages, 2003. – P. 134. – 364 p. – ISBN 966-615-125-1.
- ↑ French scientists deciphered the oak genome for the first time in world practice // TASS May 15, 2015.
- ↑ Le génome du chêne séquencé // INRA, 10.5.2015 (French)
- ↑ English oak (summer, common) – Quercus robur
- ↑ Semerikov L.F. Population structure of woody plants using the example of oak species in the European part of the USSR and the Caucasus / resp. ed. S. A. Mamaev. – M.: Nauka, 1986. – P. 48. – 140 p.
- ↑ ITAR-TASS.
- ↑ Karatygin I.V. Orders Tafrinaceae, Protomyaceae, Exobasidiaceae, Microstromaceae. – St. Petersburg. “Science”, 2002. – P. 40. – (Identifier of mushrooms of Russia). – ISBN 5-02-026184-X.
- ↑ Gvozdyak R.I., Yakovleva L.M. Bacterial diseases of forest tree species / Responsible. ed. Bila V.I.; Institute of Microbiology and Virology named after. D.K. Zabolotny Academy of Sciences of the Ukrainian SSR. – Kyiv: Naukova Dumka, 1979. – P. 28-36. – 244 p. – 850 copies.
- ↑ Yatsenko-Khmelevsky A. A., Kobak K. I. Anatomical structure of wood of the main forest-forming species of the USSR / Leningrad. forestry acad. them. S. M. Kirov. – L: RIO LTA, 1978. – P. 26-27. – 64 s. – 1000 copies.
- ↑ The Oxford Companion to Food / Alan Davidson, Tom Jaine. – Oxford University Press, 2014. – pp. 197-198. – ISBN 978-0-19-104072-6.
- ↑ Blinova K. F. et al. Botany-pharmacognostic dictionary: business. allowance / Under (inaccessible link) ed. K. F. Blinova, G. P. Yakovleva. – M.: Higher. school, 1990. – P. 186. – ISBN 5-06-000085-0.
- ↑ According to this EOL. See Body Card.
- ↑ Oak grove in the vicinity of the village of Shemakha, Website of the information and analytical system “Specially Protected NATURAL Areas of Russia”.
Reproduction
The petiolate species bears fruit at the age of 30 years. Approximately once every 7 years, fruits ripen on the branches, from which new seedlings then grow.
In the natural environment, acorns, falling in the fall, germinate within 2-3 weeks. In this case, only the root grows, and the shoot itself develops in the spring. The long taproot goes deep into the soil, so soil moisture is important. Then a stem appears, on which small but recognizable oak leaves bloom. A young oak tree looks like a blade of grass, but if the plant gets stronger, over time (it adds 25-30 cm per year) it will turn into a mighty tree.
The oldest pine trees in the world
All long-lived specimens found by scientists are protected by law. According to world research, the oldest representatives of pine are known today:
| Species name | Age, g. | Location of discovery (US state) |
| Spinous intermountain | 5069 | California |
| Spinous intermountain | 4862 | Nevada |
| Spinous intermountain | 4850 | California |
| spinous | 2443 | Colorado |
| Balfour pine | 2118 | California |
| Soft pine | 1678 | New Mexico |
| Balfour | 1674 | California |
| Soft | 1669 | Colorado |
| Soft | 1667 | Idaho |
| Balfour | 1657 | California |
| Soft | 1550 | Colorado |
Coniferous plants are decorative all year round; they have the property of purifying the air from gases. All that is needed to grow a crop is to provide conditions close to the natural environment.