Warehouse of finished products
The Institute for Standardization of Products Manufactured by Russian Enterprises pays great attention to the quality of manufactured lumber from coniferous trees. A large area of the state's territory is occupied by coniferous forests, which provides the forestry industry with immeasurable volumes of raw materials. In order to standardize the requirements for coniferous products and protect consumer rights, since 1988 on the territory of the USSR, GOST 8486-86 was introduced. All its provisions, as amended, continue to apply in modern Russia. The current standard covers all types of profile products made from softwood. The document includes technical requirements for lumber intended for use in Russia and for export.
Technical requirements
Based on appearance and structure, lumber is divided into products such as edged boards, unedged boards and timber. GOST regulates the dimensions of lumber.
For sale on the domestic market, some deviations from the ideal standard according to GOST are allowed in the dimensions of width, thickness and length of lumber.
Name of board surfaces
Timber marking
Each type of coniferous timber is assigned a specific marking, which consists of letters and numbers:
- · shape – board, timber;
- · grade - selected, first (1), second (2), third (3) and fourth (4);
- · type of wood – larch, pine, spruce, cedar and fir, general grade – xv;
- · cross-section – width and thickness in mm;
- · thickness of unedged boards in mm;
- · state standard number – 8486-84.
Note: this video will give an idea of the marking of timber ends
For example: selected timber, 40 X 40, GOST 8486-86, board 3, 32, GOST 8486-86 (for unedged boards, the width is not indicated).
Wood moisture percentage
Lumber is assigned 4 grades: selected, first, second, third and fourth. The first three are made from wood with a moisture content of about 22%. Material with a high level of moisture is produced from felled forest in the period from the beginning of May to the end of September. Coniferous profiles must be impregnated with antiseptics. GOST has not established moisture level standards for the fourth grade of wood.
Quality indicators
The quality of softwood lumber is assessed by the condition of the face and edges, choosing one of the worst boards from the entire batch of finished products. The quality of the timber is determined by the condition of the worst edge of the lumber.
The roughness of the edges of lumber of all grades is limited to 1250 microns, except for the fourth grade. For him, the norm is 1600 microns.
The dimensions of the violation of parallelism of the face and edges are allowed by the standards approved by GOST 24454. For unedged boards, an indicator relating only to the face is specified.
Quality of deck boards
A separate requirement is imposed on the deck board. Only selected varieties of larch are allowed for lumber production. It is used to make hull plating and deck surfaces of first class ships for sailing on the sea and river.
On decks of water transport, the boards must be made of sound longitudinal mid-length of the trunk. The layers are cut along the longitudinal axis of the lumber with a size of at least half and along the diagonal axis of at least a quarter of the width of the board.
As for the size of knots, fused, partially fused and unfused inclusions should be about one centimeter in size.
Current GOST standards for lumber (edged boards, timber)
The production of lumber in our country is regulated by regulatory documents that were adopted back in the middle of the second half of the twentieth century. Participants in the domestic market use more than two dozen quite current GOSTs for coniferous and deciduous species, which allows the consumer to interact normally with manufacturers and suppliers.
The task of the GOST system in this area is to formulate clear rules for determining product quality, establish requirements for the production, storage, transportation and sale of a specific product. The most popular for determining the quality of edged softwood lumber are:
- GOST 8486-86 Softwood lumber. Specifications
- GOST 24454–80 Softwood lumber. Dimensions
This lumber is GOST
Regulations for softwood lumber according to GOST 8486-86
The standard characteristics are the following indicators:
Dimensions and number of knots
The standard defines standards for the presence of various types of knots in coniferous wood. Natural inclusions in the structure of the material are divided into several types of knots:
- · fused – formations that have grown together with the main wood by 75% or more of the circumference of the knot cut;
- · unfused - inclusions are connected to the base by 25%, which causes the risk of them falling out of the layer;
- · falling out are the remains of dead branches. The presence of external falling knots is allowed only for 4th grade timber. External defects are called through knots that extend onto both layers;
- · rotten inclusions reveal themselves by their dark color and rotten, loose structure. In higher varieties their presence is unacceptable.
On the edges of selected and 1st grade lumber 100 cm long, up to 2 pieces are allowed. external knots on each face. In third-grade timber, up to 2–4 knots are allowed on each side of the product. Their number for profiles of the 4th grade is not limited. For timber, the presence of knots is also not limited by anything due to the high thickness of the cross section.
The size of knots in selected and 1st grades should not exceed 30% - 20% of the entire area of the edge width, for the third and fourth grades on half the area of the edges.
Defects of lumber
Cracks
The presence of through cracks is allowed, the size of which is limited to 10 - 20 cm. Through the longitudinal axis of lumber, through cavities from 15% to 50% are allowed for all types of wood profiles.
Damage to wood structure
Small mold accumulations and fungal colonies are allowed for all types of timber. In selected coniferous wood profiles there should be no rot at all. In material of the fourth grade, small putrefactive inclusions are allowed.
Warped
Curvatures are permissible along the length of the material in the following quantities:
- · selected, 1st, 2nd – 0.2%;
- · 3rd – 0.4%;
- · 4th – not limited.
Note: be sure to watch the video “Automatic sorting of timber”
Lumber GOST 18288-87
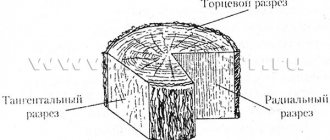
GOST 18288-87, which defines the basic terms used in the sawmill industry, can be very useful for an inexperienced user. In particular, this standard explains the concepts of tangential and radial cutting, helps to determine the difference between face and edge, edge and end, edged and unedged product.
He describes what wane is. GOST 18288-87 contains information about the need to standardize load-bearing capacities for structural lumber; the document defines various types of boards, beams, beams...
Characteristics of softwood timber
Technical characteristics of coniferous timber include six items:
Assortment
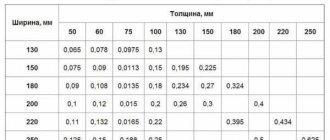
The list shows two main parameters - width and thickness. Dimensions change upward in approximately 25 mm increments.
For boards, the minimum thickness is 16 mm, the maximum section height is 75 mm. The width of the edged board ranges from 75 to 275 mm.
The timber is produced from 30 x 30 mm to 250 x 250 mm. Also, the cross-section of the timber can be rectangular.
Density
Spruce and fir profiles have the minimum density. Their specific gravity is approximately 440 kg/m3 and depends on the level of humidity (maximum 12%). The average density of pine is 590 kg/m3. The heaviest coniferous tree species is cedar (650 kg/m3).
Weight
Softwood profiles are sold by measuring the product in cubic meters. To find out how much purchased timber weighs, just multiply the volume by the specific gravity.
Note: The weight of wood varies depending on the moisture content of the material. The parameter is adjusted using a special table.
Length
The maximum length of forest products produced from deciduous trees is 5 m. Coniferous trees have a lower specific gravity than other wood. Therefore, these lumber is produced up to 6.5 m in length. The lighter the wood, the longer the product.
Strength
The strongest coniferous wood is larch. It is 1.5 times stronger than pine.
Ecology
The internal fences of buildings lined with coniferous lumber exude a pleasant pine aroma. Wood fumes kill harmful microorganisms in the room atmosphere.
Lumber GOST 2140-81
GOST 2140-81 “Visible defects in wood” makes it possible to understand what should generally be considered a defect (a defect that limits the use of lumber or reduces its quality).
For convenience, in this regulatory document, defects and defects are divided into groups:
- bitches
- cracks,
- Chemical stains,
- Fungal infections
- Defects in the structure of the trunk,
- Defects in the structure of wood fibers,
- Warping,
- Foreign inclusions,
- Processing defects and mechanical damage.
It is very important that GOST 2140-81 not only lists all existing defects in wood, lumber and wood parts, but also provides methods for measuring their size and quantity. Using the information from this standard, it is much easier to determine the quality of lumber, it is much easier to understand the tables of GOST 8486-86 - namely, what grade the board or timber belongs to.
Photos of visible flaws and defects in lumber
Classification of lumber
All types of lumber are divided into categories according to the method of preparing the goods for sale. If the wood is end grain, it will be stacked with equal lengths of logs. The cuts are smooth, directed perpendicular to the axis. Uncut wood is represented by trunks of different lengths, with uneven cuts.
Calibrated building material consists of stacks that have been air-dried before cutting. For deciduous trees the humidity norm is 20%, for coniferous trees – 22%. One of the operations may be antiseptic treatment.
Planed logs - sanded for better drying, planed flat or in fragments. Structural materials are called hardwood - oak and larch.
Based on the thickness of the log, it is unraveled in accordance with the developed cutting map, providing a greater yield of sized edged boards or timber.
Receive:
- two-, three-, four-edged timber;
- a clean edged board with a blunt or sharp wane;
- bar;
- both floors are slab and plank;
- edged sleeper.
The grade of cut assortments is regulated by relevant standards.
Lumber GOST 3808.1-80
This standard is called “Softwood lumber. Atmospheric drying and storage." It states that purchased lumber of natural moisture must be treated with an antiseptic before laying it on site. GOST 3808.1-80 describes the principles of atmospheric drying and helps to properly organize the warehouse space (including the design of foundations and roofs).
The developers paid special attention to the rules for the formation of packages and stacks, where they indicated:
- methods of relative arrangement of lumber;
- the size of the necessary gaps to ensure ventilation;
- type, dimensions, location and number of spacers.
Having familiarized yourself with the provisions of GOST 3808.1-80, it will not be difficult for you to finish drying the lumber yourself. You will be able to store the purchased board/timber at your site without loss or understand whether the seller handles his product correctly.
Regulations for lumber storage
General information about lumber
It is not enough to fell and remove the tree from the cutting area. It is necessary to cut the whip into separate ridges aligned in thickness in order to separate its parts as completely as possible. Unedged boards are obtained by sawing a log lengthwise and leaving sharp wane on the boards at the ends - the edge repeats the expanding silhouette of the cut.
From each trunk you can get a cut out tetrahedral core and external fragments in the form of 4 slabs - layers uneven in width on one side and an unbarked cylindrical surface on the other. The internal parallelepiped can be used as a tetrahedral beam or cut into boards - this is edged lumber.
The name of the fragments and their geometric relationships correspond to GOST 18288:
- face - a wide, long surface, inner and upper;
- edge - the outer boundary of two layers along the length;
- end - the distance between the layers along the narrow part;
- board – thickness up to 100 mm, width more than double thickness;
- timber – thickness and width more than 100 mm.
- block – up to 100 mm thick, up to 200 mm wide
It is customary to indicate the length of lumber in meters, thickness and width in mm.
It is important to know what type of cut the board was made from. Schemes for cutting central, core and side fragments are used. The best material is considered to be core timber or board for structures made from the central part. For finishing work, side blocks with a bright ring pattern are used.