Autumn brings with it a special mood. In nature, everything calms down and prepares to go to winter sleep. Trees in the rays of the autumn sun look amazingly elegant. But aspen in autumn looks more colorful than others. This species can have a wide variety of crown colors, creating an indescribably wonderful picture that nature gives to everyone. Walking through an autumn park or forest where aspens and other trees grow will be just a great idea. Observing the beauty of the world around you, you can get a lot of positive emotions and recharge with a positive attitude.
Botanical description
Common aspen (Populus tremula L.) is a deciduous tree. Height: 25-30, up to 35 m, diameter: 50-100 cm. The root of the common aspen is powerful, located deep, forming root shoots.
The trunk is columnar. The crown is ovoid or broadly cylindrical. The bark of common aspen is smooth; in older trees it has cracks closer to the roots. Color: light green, greenish-olive, greenish-gray, dark gray at the root in old trees. Young branches are not pubescent. Wood: white, with a green tint.
The buds are small, pointed, sticky, initially hairy, then bare. Color: brownish.
The leaves of common aspen are alternate, large, glabrous, rounded at the base, with pinnate venation. On long branches they are rounded or triangular-ellipsoidal, coarsely cut; on short branches they are rounded-triangular, short-pointed, serrated, sometimes with sparse silky hairs. Length: 3-7 cm, for coppice shoots - up to 15 cm. Petioles are long, flattened laterally in the upper part.
Common aspen is a dioecious plant. Flower buds are large, ovoid. The flowers are small, inconspicuous, collected in dangling furry earrings. Men's are reddish, women's are thinner, greenish. Length of earrings of common aspen: 4-15 cm, thickness: 2 cm.
The fruit is a very small capsule. The seeds are equipped with a tuft of white fluff. Black color.
Common aspen blooms before the leaves bloom, in March-May. The seeds ripen in 35 days and are dispersed by the wind. Leaves appear 20 days after flowering.
Reproduction of common aspen: seeds, root suckers.
What does an aspen tree look like?
From a distance, aspen may look like an ordinary birch, because it also has a light trunk, mostly grayish or light green.
The bark of younger trees, as a rule, is much smoother, and with age it acquires numerous cracks running upward from the root zone.
- The leaves of this tree are quite large, rounded, jagged, bronze green in color, and the petioles are flattened in the middle and oblong.
- Over the life cycle of a tree, leaves tend to change their shape from oblong in youth to rounder in old age.
In autumn, the foliage takes on a bright golden color. The aspen stretches upward with its crown, dense branches grow to the sides. Due to the specific structure of the petiole, the foliage begins to sway even from the slightest breath of wind.
Maple leaf color in autumn. What color are the leaves in the autumn
Autumn is a bright period in nature, when the forest changes the color of the leaves from green to yellow, red and brown in a matter of days.
What explains the riot of colors during the leaf viewing season? Why do some trees turn yellow, others turn red, and then they turn brown.
The explanation lies in the replacement of chlorophyll with other substances: carotenoids and anthocyanins. In summer, trees have a lot of nutrients, but with the arrival of autumn, this supply gradually decreases. With the depletion of reserves, the synthesis of chlorophyll stops. And then other pigments that are present in the leaves, but overlapped by the green color - yellow and orange - become noticeable. These are the same pigments that determine, for example, the color of carrots - carotenoids.
Leaves with red hues are the result of the formation of anthocyanins. These pigments are absent in green leaves. They begin to form in the leaves of some plant species after the disappearance of chlorophyll. Anthocyanins are the same pigments that give radishes, geraniums, roses or cauliflower their color.
The brightness of the color of autumn leaves depends on the weather. Trees wear their most beautiful clothes in sunny, dry weather, at temperatures of 0 – 7 degrees Celsius. If the weather is cloudy and rainy, then the leaves do not burn, but turn into dull yellow shades or even turn brown.
As winter approaches, yellow and red leaves gradually lose their pigments. Brown leaves, which can be seen in late autumn, with the onset of severe cold, after snowfall, are leaves in which there are no pigments left at all, and the cell walls have become noticeable.
Characteristics of trees of the aspen genus
The average life of a tree is about 100 years, during which time it manages to grow up to 30-40 meters. The wood has a whitish tint, and at the site of the log house it even gives off a blue tint (there is a version that it was because of this blue color that aspen got its name).
- The tree is considered a fast-growing tree; at the beginning of its life it can grow 40-80 cm every year.
- Aspen is highly valued by woodworkers because it is a soft wood that is quite easy to work with and cut.
Another advantage is aspen’s resistance to moisture. Wood can be preserved in water for a long time, and when dried it does not crack.
Moreover, when wet, it becomes even more amenable to processing and carving; this can be done even with a well-sharpened knife.
Why is he shaking?
With a slight wind, the foliage of a tree begins to oscillate, resembling trembling in nature. People have the expression “trembling like an aspen leaf.” The fact is that the leaf plate is flat, and the cuttings on which the leaf is located are flat.
Unlike other plants, the leaf and stem are not flexible and begin to vibrate when the wind blows lightly. Therefore, it seems that the tree is trembling.
An adult tree often rots; the process begins gradually and as it grows, the trunk becomes hollow inside. Therefore, during strong winds, damaged trees often break.
For wood
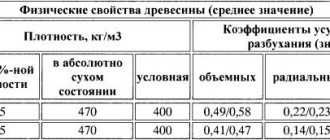
The wood is light, loose and soft, does not burn easily and does not smoke. Compared to other poplars, the wood is denser, colored evenly across the entire width of the trunk, and there is no core. Longitudinal sections show narrow stripes and spots; the vessels are evenly distributed throughout the annual layer. Aspen wood can be confused with linden. They are determined by the shade - in linden it is pinkish, and in aspen it is greenish. In addition, the pith rays of aspen are not visible.
Aspen wood is currently used in the match industry, for the production of cardboard, plywood, and for the construction of cellars. The rock logs rot quickly and are rarely used in construction.
Unlike other trees, the species is not resistant to heart rot, which infects wood through mechanical damage and through broken branches. The causative agent of the disease is the aspen polypore fungus. Populus tremula can be distinguished from other species by the fruiting bodies of the tinder fungus - the parasite is found only on aspen. The disease causes stem damage, weakening of the plant and deterioration in wood quality.
The difference between aspen and poplar
It is not difficult to find signs of how poplar differs from aspen. There are several reliable signs:
- Branches from both trees with dormant buds broken in early spring should be placed in a glass of water. The poplar will be the first to start growing and spread its sticky leaves, while the aspen will wake up later and its leaves will not have such a pronounced shine.
- The aspen blooms first, followed by the poplar. Moreover, only the poplar will give abundant fluff.
- The structure of leaf petioles in the two species is different: aspen petioles are long and easily tied into a knot, while poplar petioles are short.
- Aspen branches are more fragile and break easily from force, while poplar branches are more likely to bend than break.
- If you compare the leaves, they have a lot in common, but there are also differences - the shape of the poplar leaf is more elongated and pointed.
Spreading
Aspen grows in large quantities on the border between the tundra and forest zones, as well as in the forest-steppe. The plant prefers to grow along the banks of reservoirs, on forest edges, in ravines, in mountainous and swampy areas, and can rise to the very top border of the forest zone. Being an unpretentious wild-growing form, it takes root more readily in well-moistened soils, although it does not die under conditions of steppe drought. The lack of light is critical, which causes the crown to quickly fade.
Aspen is not capricious and freely coexists with coniferous and various deciduous species. In the free steppe zone, one tree quickly forms an entire colony of root shoots, and the distance from the mother plant to the shoots can reach 30-40 m. Such groves are not afraid of fires, since the roots remaining deep in the ground in the spring give rise to a young population that grows at a speed of up to 1 m per year in height.
In the southern regions, where there is enough light and moisture, aspen competes with other slow-growing species: oak and conifers. Especially often its dense thickets can be found in areas where industrial logging took place. Therefore, replacement species are planted as soon as possible to prevent the uncontrolled spread of aspen trees.
Aspen grows over a vast territory of the temperate climate zone from Europe to China, in Kazakhstan and Mongolia, is found in Korea, and grows everywhere in Russia. In the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, the plant is included in the Red Book.
By bark
The bark of young Populus tremula is smooth, gray-green, darkens with age, and shallow cracks appear at the bottom of the trunk. You can recognize aspen by the olive tint of its bark; in most other types of poplars it is dark gray at the bottom of the trunk and light gray above. You can also distinguish aspen from alder by comparing the bark. Alder bark is dark brown, in rare cases gray. In the dark, the light bark of Populus tremula can be confused with birch, but the birch has a lighter, bright white trunk. However, in the southern zone of Russia there are single specimens of dark-barked aspen.
The bark is used in folk medicine; it contains large quantities of phenolic substances. According to modern research, the plant bark increases the excretory function of the kidneys, has a diuretic and antiulcer effect, and helps relieve inflammation.
Aspen propagation: features
We are interested in the details of the propagation process of a tree called aspen.
Its seeds have a very low level of endurance, and become unsuitable for use after just a few days, from the moment they fall out of the boxes.
An important condition for successful germination is a sufficient level of moisture in the soil.
Only once on such soil do the seeds have a chance to grow. If the ground is covered with leaves, the grain will simply get stuck halfway and die.
Such conditions do not make every area of soil suitable.
Therefore, young animals grown from seeds are not such a common sight. They are found in places where the soil has been plowed, loosened and sufficiently moistened. There are simply none in the forests.
How aspen creates forests: propagation by root shoots
When you have the opportunity to visit an aspen forest, take a close look at the already mature specimens of this wood.
Reproduction of aspen in forests occurs, in the overwhelming majority, with the help of long systems of roots and shoots scattered throughout the plant’s habitat.
Somewhere nearby, a young shoot will definitely appear, very similar to a poplar. The height of the shoot is approximately up to the knee for an adult.
And how did they get here:
- To answer this question, you need to take a shovel and carefully clear the ground around the young tree.
- You'll see something interesting. A long and thick cable-like root of an adult aspen will run through the ground. It is from this that this green aspen tree originates.
- Such a root can grow and stretch quite long distances in any direction.
- If you really want to, you can dig out the path from the root to its tree and see how many offspring it has produced.
- Young aspen trees are shoots that originate from the roots of the mother tree; they are also called root shoots.
For your information. Just one such root can produce more than ten or more young trees. Their arrangement resembles balls on a string, arranged at significant intervals.
A new sprout appears at a distance of more than 35 m from the mother tree. At such a distance, it can be difficult to find and correlate a specific tree and sprout, especially in a forest, with its root routes.
Propagation by seeds in this case has very low efficiency.
Benefit
A tree such as aspen, whose leaves help provide shade in the summer and brighten the area during autumn days, is valued primarily as timber. Since this tree grows quickly, it is used for landscaping.
In winter, hares and moose feed on the bark of this woody plant, and this helps them survive frosts.
When all the leaves on the trees and bushes have changed color. What color are the leaves in the autumn
Autumn is a bright period in nature, when the forest changes the color of its leaves from green to yellow, red and brown in a matter of days.
What explains the riot of colors during the leaf viewing season? Why do some trees turn yellow, others turn red, and then they turn brown.
The explanation lies in the replacement of chlorophyll with other substances: carotenoids and anthocyanins. In summer, trees have a lot of nutrients, but with the arrival of autumn, this supply gradually decreases. With the depletion of reserves, the synthesis of chlorophyll stops. And then other pigments that are present in the leaves, but overlapped by the green color - yellow and orange - become noticeable. These are the same pigments that determine, for example, the color of carrots - carotenoids.
Leaves with red hues are the result of the formation of anthocyanins. These pigments are absent in green leaves. They begin to form in the leaves of some plant species after the disappearance of chlorophyll. Anthocyanins are the same pigments that give radishes, geraniums, roses or cauliflower their color.
The brightness of the color of autumn leaves depends on the weather. Trees wear their most beautiful clothes in sunny, dry weather, at temperatures of 0 – 7 degrees Celsius. If the weather is cloudy and rainy, then the leaves do not burn, but turn into dull yellow shades or even turn brown.
As winter approaches, yellow and red leaves gradually lose their pigments. Brown leaves, which can be seen in late autumn, with the onset of severe cold, after snowfall, are leaves in which there are no pigments left at all, and the cell walls have become noticeable.
Contraindications
There are no serious restrictions on the use of aspen. The only thing is that aspen decoction is not advisable for people who have any digestive system disorders.
In addition, sometimes it happens that a person has an individual intolerance to this decoction. Therefore, before being treated with traditional medicine, it is better to consult a specialist.
So, we hope we have answered all your questions about aspen. Learn, explore and enjoy nature!
Tree care
Proper tree care involves choosing the right place to plant it and watering it. The plant is planted in the ground in the form of seedlings or seeds. Seedlings are transplanted in the spring to give them time to take root in a new location. Aspen is not picky and quickly takes root. It is planted away from residential structures, since due to the early appearance of rot in the trunk, the tree can easily collapse. The fluff during flowering causes an allergic reaction in some people.
Aspen seeds
The distance between each planting hole must be at least 2 meters. Otherwise, instead of trees, the seedlings will grow into a single bush. The recesses themselves should be shallow.
It is important to have an additional drainage layer of 8-10 cm from crushed stone or pebbles. With its help, the soil will retain moisture and create favorable conditions for aspen growth.
For the full development of seedlings, it is worth ensuring:
- correct choice of soil. Fresh, fertile and well-draining loamy or sandy loam soil is suitable;
- regular watering of the plant. Artificial cultivation of aspen requires periodic soil moisture. During dry periods, watering should be plentiful. The tree cannot tolerate dry soil;
- feeding It is applied at the stage of transplanting seedlings or planting them in the ground. Subsequent application of fertilizers is not required due to the powerful and well-developed root system. More often, mullein is used in a ratio of 1 kg per 20 liters of water and superphosphate - 20 g per the same amount of liquid;
- pruning thick branches from February to April. Young branches can be cut all year round;
- cutting down mature trees over 50 years old. Young shoots quickly appear around their stumps.
The soil at the site where the seedlings are planted needs additional loosening and weeding. Proper care will accelerate the growth of young aspen and its healthy development in the future.
Interesting facts about aspen
It is believed that the name aspen itself comes from the word “blue”. Our ancestors also noticed that the place where a tree was cut turns blue. In ancient times this was given magical significance. However, modern scientists have found that this is a chemical reaction to the interaction of tannins contained in wood with the metal of an ax or saw. The interesting texture of wood is highly valued by craftsmen, who use wood as a material to create objects for various purposes.
The Latin name of aspen - Populus tremula - is translated into Russian as “trembling man”. This is what they say about a frozen or frightened person - he trembles like an aspen leaf. There is a widespread belief that the property of a tree to flutter its leaves even in calm weather is due to the fact that the traitor of Jesus Christ, Judas Iscariot, once hanged himself on it. And, according to superstition, with every memory of this terrible event, the aspen tree begins to tremble in fear.
However, as scientists have found out, this tree never grew in Palestine: neither in biblical times, nor in our days.
Experts explain the property of leaves to flutter simply. It's all about the structure of the leaf. Anyone who has looked closely at what an aspen tree looks like has noticed that its leaves are relatively wide and dense to the touch, while the petioles are very long and flexible. That's why they can't keep their leaves straight. This simple fact explains the sensitivity of aspen to any air movement.
To believe or not to believe in mysterious forces is everyone’s personal choice. However, it cannot be denied that this tree is beautiful at any time: during the time of flowering of catkins, and in the summer, when the rustling of leaves can be heard even in the calm, and during the autumn leaf fall. To observe how the tree looks throughout the year, it is worth planting an aspen near your entrance or home.
Where is it used?
Populus tremula is a necessary plant that benefits humans. A fast-growing crop with bright autumn foliage will become a noticeable feature of a park or alley. The species is often combined with spruce and birch trees, creating beautiful landscape compositions.
Aspen is used to restore local crops destroyed by fires. Young shoots are planted in groves of Populus tremula. The species gradually develop under spreading trees, without suffering from the bright sun. After the young animals overtake, the adult specimen dies in the shade. The technology facilitates the regeneration of spruce, oak and birch forests.
Beautiful area Source rastenievod.com
Bees collect pollen from flowering aspen catkins, and glue for processing propolis from the buds. The young shoots are eaten by deer, elk and hares. Bird hollows are hollowed out in soft wood. Birds and bats live in old high-altitude burrows.
Aspen is used in turning and carpentry. The material is very soft, so it is easy to plan, saw and shape it into the desired shape. Artificial flowers are created from wood shavings. The raw material has good antibacterial properties; it is used to make:
- tableware;
- barrels;
- vats.
Aspen is used for leather processing. Green and yellow dyes are obtained from the bark. Wood is taken both for the construction of houses and utility buildings, and for the assembly of garden furniture. Planks are suitable for roofing work. The raw materials are used to create pulp, containers and plywood.
Aspen utensils Source livemaster.ru