Wood is recognized as one of the safest materials for human health used in construction and in the manufacture of various furniture. Its environmental friendliness can be rated five points, which significantly expands the scope of use of wooden products. Wood can be used to produce workpieces of various shapes and sizes. Special technologies for working with wood help with this. These technologies also include wood bending and gluing, which is widely used in the modern production cycle.
Why is wood splicing and bending necessary?
The entire woodworking process takes a significant amount of time. First, the wood is dried, sawn, treated with special compounds - all this happens at woodworking enterprises. Subsequently, boards and other materials are prepared from wood.
These blanks are sent to factories, where they are used to make special construction materials or various furniture. During the production process, wooden blanks of different shapes and sizes may be required, and therefore woodworking techniques such as bending and gluing are widely used.
Bonding is used to produce parts of the desired size and shape. Wood splicing can be done by width, length or thickness. Pre-prepared ends of the workpieces can have special grooves or tenons, which increases the strength of the parts being connected. Different types of wood glue are used in the gluing process.
Wood bending is necessary to produce curved parts. You can bend wood manually, subject to certain features of this work, or on special machines.
The strength and practicality of wooden products, for the manufacture of which special machines for gluing or bending are used, can be rated at five points. Woodworking factories always try to follow all the technology of working with wood, and therefore the goods produced are of high quality.
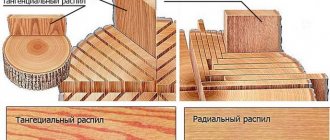
Photos of the wood processing methods described above
Splice
Gluing
bending
Main stages of gluing technology
Gluing is the main process of working with wood in any furniture production. In order to obtain a durable and high-quality workpiece, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the entire technology of the process of connecting individual parts. The accuracy of all work is also necessary to prevent possible subsequent deformation.
The process of joining wood and products made from it consists of several stages:
- Preparation of the blanks themselves.
- Selection and application of adhesive composition.
- Actually the gluing itself.
Preliminary preparation of wooden blocks and other workpieces consists of creating special tenons or grooves in them, which can be done using a special tool - a milling cutter.
Using a cutter to join wood
Milling is a fairly old branch of wood processing. The first milling machines appeared more than three centuries ago. Today, milling is an indispensable and universal method of wood processing.
For this woodworking machine, you can choose cutters of different shapes - sharpened elements with different types of blades. Using these cutters, various parts are made.
In the gluing process, milling machines are necessary for:
- Cutting tenons of different shapes, with the help of which individual workpieces will be glued together in the future.
- Creating holes in the material. Creating folds and grooves, which are also necessary in the process of manufacturing parts of different shapes.
Milling machines are used everywhere, they can be either manual or electric. The ease of making wooden blanks for gluing using a machine can be rated four points. In order to obtain an accurate workpiece, you first need to gain some experience.
This video provides an overview of cutters for splicing wood and making technological connections. Shown are cutters for straight and angular splicing, as well as a microtenon, zigzag and wave cutter:
Automatic line for wooden blanks
Splicing lumber in any production allows you to create high-strength materials with new, sought-after qualities and also allows you to rationally manage production waste.
Automatic splicing lines include several sequentially operating machines, which ultimately make it possible to obtain the material of the required length and width from short blanks. With the help of a splicing line, glued laminated timber, which is popular today, is produced.
The entire technological process when using a production line for splicing wooden blanks consists of several stages, which are provided by a complex of machines included in the installation:
- The cutting press machine provides the required dimensions of the material.
- A router prepares tenons and grooves in wood pieces.
- The gluing installation distributes the glue in accordance with the set parameters.
- The cross-cutting machine completes the gluing process.
Using a splicing line in furniture factories ensures high productivity and reduces the number of jobs. The appearance of products obtained using automatic machines can be rated five points, since the entire process is strictly controlled.
This is how an automatic length splicing line works:
Types of glue
The correct selection of the type of glue determines the quality of joining wooden workpieces. The choice of glue also depends on the type of wood being glued and the shape of the workpieces. Waterproof adhesive compositions are most often used.
The furniture industry uses several types of synthetic adhesives:
- Thermosetting adhesives are used for gluing tenon parts without heating. The basis of these types of glue are liquid resins.
- Phenol-formaldehyde adhesives are used for gluing wood boards, wooden blanks and plywood.
- Epoxy adhesives are mainly used for joining wood with other materials - metal, plastic.
- At woodworking enterprises, glue based on urea resins is most often used. Also often used are adhesive compositions in powder form, which require preliminary preparation.
Bonding of parts is carried out coldly and by heating them. To glue workpieces along the edges, adhesive film is often used; it comes in sheets of various sizes.
Before gluing, the parts must first be prepared, that is, degreased, removed dirt and various types of stains. After applying glue over the entire surface and connecting the required workpieces, the parts are clamped using special devices, which are removed only when completely dry.
Machine tools
To splice glued wood, special machines in the form of presses can be used. They clamp the parts for the required time. This ensures a strong connection between the adhesive surfaces and prevents movement of parts. The press can be selected according to the length of the beam, power, and the presence of additional functions.
Molecular adsorption theory
A further development of the theory of adhesion was the adsorption theory developed by McLaren and Debroin. This theory explains the formation of a strong adhesive seam by the manifestation of a specific intermolecular interaction - free surface energy.
Adhesion is considered as a process that occurs exclusively on the surface of the body, similar to the adsorption process. The connection between the adhesive (glue) and the substrate (substrate) is explained by the action of van der Waals forces, the degree of bond strength is explained by the direct interaction of certain functional groups of molecules of the adhesive and the substrate. This theory is based on a well-known empirical rule, according to which it is assumed that high adhesion can occur only in two cases: when the molecules of the contacting bodies have polar functional groups and when the molecules of the adhesive and the substrate are non-polar. If nonpolar and polar substances interact with each other, then adhesion should be small. However, practice and research show that this rule is not always followed accurately, since the influence of other equally important factors is not taken into account: the number of contact points and the distance between them. These parameters are known to depend on the mobility of molecules—the rate of diffusion of polymer chains.
This rule also does not take into account the possibility of the formation of hydrogen bonds between polar groups of adjacent molecules belonging to the same phase. The occurrence of hydrogen bonds, naturally, sharply reduces the high adhesive interaction inherent in polar groups: –COOH, –OH, –NH2, –OOCCH3, etc. The possibility of polar groups closing on themselves is not taken into account - the formation of hydrogen bonds between adjacent polar groups and groups belonging to the same molecule. This also dramatically weakens the adhesion of molecules.
Gluing wood at home
Wood gluing may sometimes be required at home. This often happens when wooden furniture sets are put up or due to various breakdowns. Before gluing, the surfaces of wooden products must be properly prepared.
To do this, their pores are cleaned of old glue and paint layers, degreased with a solvent, and dried. After applying glue to both parts, they are carefully connected and clamped in a clamp for at least 30 minutes.
Commonly used adhesives include:
- Casein glue.
- Waterproof seams are provided by synthetic wood glue.
- Strong bonding is obtained when using glue “Dubok”, “Ago”, “Mekol”, “Mars”.
In order to achieve high strength of the parts to be glued, it is necessary to strictly follow the instructions included with each type of glue.
You can clearly see how wood is glued together in the video:
Diffusion theory
The diffusion theory of adhesion, proposed by S. S. Voyutsky, interprets the formation of a strong adhesive bond through the action of intermolecular forces that appear during the interpenetration of macromolecules due to their diffusion, contributing to an increase in molecular contact. For example, diffusion of one polymer into another to a depth of 0.5–1.0 nm increases the contact area by 3–5 times. Moreover, the longer this process and the higher the temperature, the more perfect the arrangement of molecules will be and, consequently, the higher the strength of the connection.
As a rule, glue has the ability to diffuse. But if the latter is applied in the form of a solution to a material that itself is capable of swelling and dissolving, then diffusion of molecules of the bonded material into the glue is also possible. As a result, the boundary between them disappears and a strong adhesion is formed, which is a gradual transition from one polymer to another. The results of a quantitative test of this theory turned out to be quite satisfactory. The diffusion of macromolecules of two polymers has also been proven experimentally using electron microscopy.
In conclusion, we emphasize that this theory mainly reveals the kinetics of the formation of an adhesive bond and is valid only for explaining the adhesion of more or less mutually soluble polymers. Therefore, this theory is unsuitable for explaining the formation of a strong bond, for example, between a polymer and a material such as wood.
Bending technology
Wood bending can be defined as the process of bending layered or solid pieces of wood to give them the desired curved shape. Bending technology is based on the plastic qualities of different types of wood. Curvilinear wooden parts can also be obtained by processing on special machines, but this method is rarely used, as it is endowed with a number of negative consequences.
Process description
Hardwood such as oak, beech, and ash has greater plasticity. Therefore, mainly the species of these trees are used for the manufacture of curved parts. There are cold and hot bending of wood.
Hot bending is based on a sharp increase in the plasticity of wooden blanks when they are heated from 80 to 120 degrees. This heating mode is achieved by boiling in water or steaming.
The wooden blanks plasticized in this way are bent according to the prepared template and secured with clamps, after which they are cooled and dried. When bending, the convex side is stretched to the required level, and the concave side is compressed. Thick workpieces are bent using special machines.
Cold bending is used to produce multilayer curved bent parts. To obtain a part of the desired shape, you need to place several blanks coated with glue on top of each other, give them the required shape and, using a press machine, wait the required time. The shape of blanks obtained by cold bending is retained longer.
This video will show you how curved wood is made:
Relaxation theory
The relaxation theory proposed by N.I. Moskvitin (USSR) is also relatively new and has not yet received wide recognition.
It attempts to explain adhesion taking into account all types of chemical and intermolecular bonds. According to this theory, the most important factor that has a significant impact on the adhesion of polymers is stress relaxation both during contact of the adhesive with the bonded surface and during deformation of the joint during its operation. Analyzing the approximate values of the molar energies of the main types of bonds, kJ/mol: intermolecular – 13–33, hydrogen – up to 73, chemical – 110–1050, it should be noted that chemical bonds are the strongest.